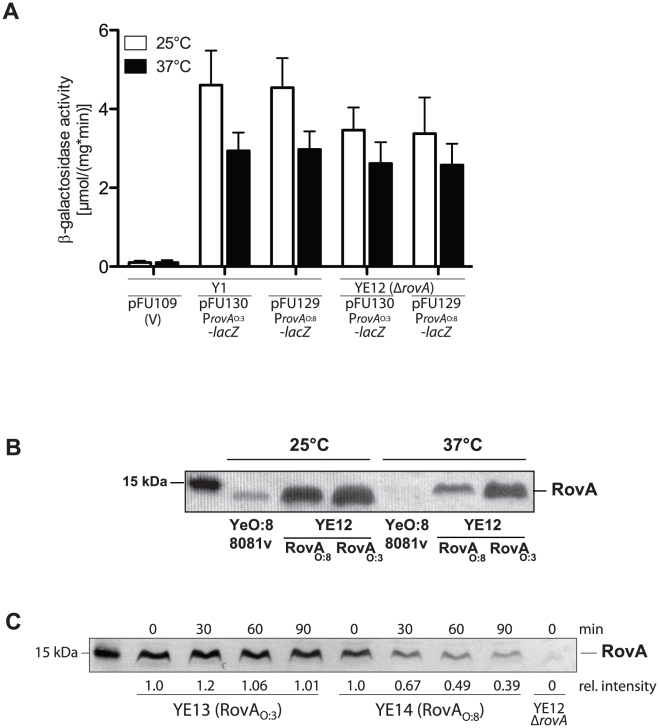
Figure 10. Analysis of RovA production and stability in Y. enterocolitica O:3.
(A) Y. enterocolitica strains Y1 and the isogenic rovA mutant of Y1 (YE12) harboring plasmids encoding the promoterless lacZ gene or the ProvA O:8-lacZ or ProvA O:3-lacZ fusions were grown at 25°C and 37°C overnight. The beta-galactosidase activity determined from the cultures is given in µmol min−1 mg−1 and represents the mean ± standard deviation of at least three independent experiments. (B) A Y. enterocolitica O:3 ΔrovA mutant strain (YE12) harboring the rovA encoding plasmids pFU119 (rovA O:3) or pFU138 (rovA O:8) and YeO:8 strain 8081v were grown overnight at 25°C and 37°C. Whole cell extracts were prepared from the cultures, separated on SDS-polyacrylamide gels and analyzed by western blotting using polyclonal antibodies directed against RovA. As a molecular marker the PageRuler Prestained Protein Ladder was loaded on the left. (C) Isogenic Y. enterocolitica strains YE13 and YE14 expressing the RovA wildtype protein or the RovAS98P derivative were grown to exponential phase (OD600 = 0.6–0.7) at 37°C before gentamicin (50 µg ml−1) and tetracycline (50 µg ml−1) were added. The cultures were incubated at 37°C for additional 90 min. Aliquots of the cultures were removed at the indicated times thereafter, whole cell extracts for identical numbers of bacteria were prepared and intracellular RovA was visualized by western blotting.