Fig. 1.
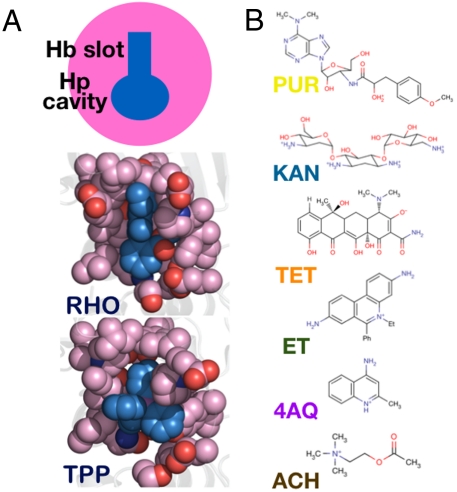
Structural and solution-based analyses of drug recognition by BmrR. (A) Schematic of noncanonical MD-binding model. The drug pocket is divided into two functional units: a hydrophobic slot located at the top front of the pocket and an adaptable, solvent-accessible, polar vestibule. (B) The chemical structures of the probes used in this study. The color and abbreviated naming scheme shown is used throughout the paper. All (crystallographic) figures were generated using Pymol (40).