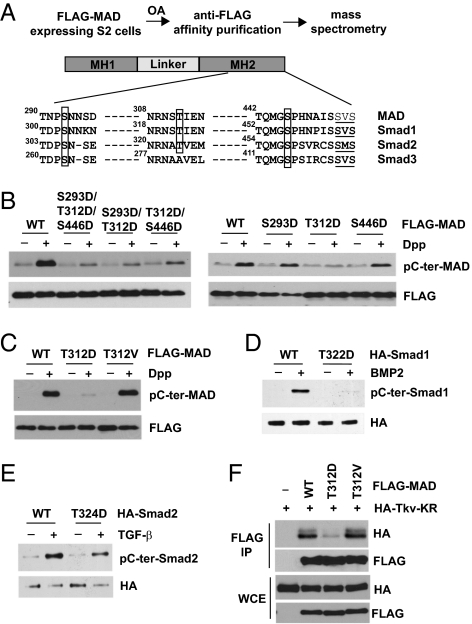
Fig. 1.
Identification of a phosphorylation site in Smad that suppresses TGF-β/BMP-induced C-terminal phosphorylation. (A) Mass spectrometry identified phosphorylation sites in MAD. Drosophila and mammalian Smads sequences are aligned, with the newly identified phosphorylation sites boxed. The C-terminal SXS motifs that are phosphorylated in response to TGF-β/BMP are underlined. (B and C) Single, double, or triple mutants and WT MAD (all FLAG-tagged) were transfected into S2 cells. After Dpp treatment (1 nM, 1 h), FLAG-MAD was immunoprecipitated and analyzed for C-terminal phosphorylation. (D and E) WT and mutant mammalian Smad1 or Smad2 (HA-tagged) were transfected into COS1 cells. After treatment with BMP2 (100 ng/mL, 1 h) or TGF-β (100 pM, 1 h), HA-Smad1 or Smad2 was immunoprecipitated and analyzed for C-terminal phosphorylation. (F) WT and mutant MAD were expressed in S2 cells along with the catalytic mutant of Tkv. Whole cell extracts (WCE) were immunoprecipitated by anti-FLAG, and the bound proteins were evaluated using the indicated immunoblots.