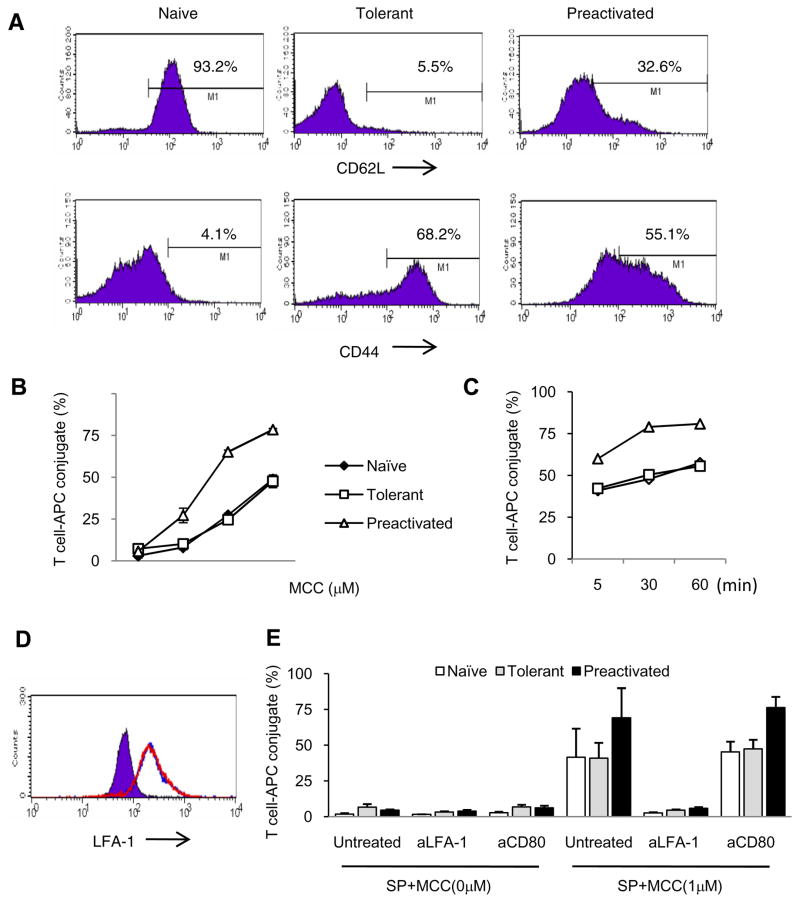
Figure 1. Phenotype and conjugate formation of adaptively tolerant T cells with spleen cells.
A, Purified naïve, adaptively tolerant, or pre-activated 5C.C7 T cells were stained with anti-CD4, anti-Vβ3 and anti-CD62L or anti-CD44 mAb. Expression of CD62L and CD44 on Vβ3+CD4+ T cells is shown. Percentages of CD62Lhigh and CD44high T cells are indicated.
B and C, Splenocytes from B10. A CD3ε−/− mice were pre-pulsed with 0, 0.01, 0.1, or 1μM MCC(88–103) peptide and mixed with naïve (◆), tolerant (□), or pre-activated (Δ) T cells for 30 min (B) or pulsed with 1μM MCC(88–103) peptide and mixed for 5, 30, or 60 min (C). The cells were harvested, fixed and stained with anti-CD4 and anti-MHC class II. The percentages of MHC class II+ cells within the CD4+ T cell population were determined. The data shown in B are the averages from 2 experiments. The data in C are all from one experiment.
D, The expression levels of LFA1 on the surface of CD4+ and Vβ3+ cells from purified naïve (purple), adaptively tolerant (blue line), or pre-activated T cells (red line) were determined by FACS.
E, The splenocytes from B10.A CD3ε−/− mice were pre-pulsed in the presence or absence of 1μM MCC (88–103) peptide and mixed with purified naïve, adaptively tolerant, or pre-activated T cells for 30 min in the presence or absence of anti-LFA1 mAb (1μg / 2 × 105 cells) or anti-CD80 mAb (2μg / 2 × 105 cells). The percentages of CD4+ and MHC class II+ conjugates were determined. The results shown are the means ± SD for three experiments.