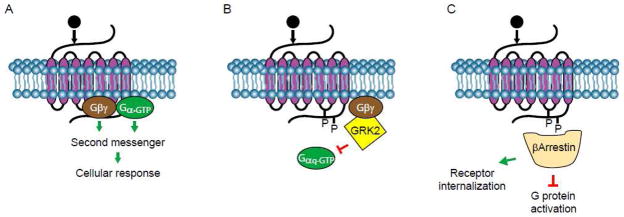
Figure 1. Classical signaling by G protein-coupled receptors.
A, Binding of ligand agonist promotes coupling of the receptor to heterotrimeric G protein leading to the exchange of GDP for GTP on the α subunit. Both Gα-GTP and Gβγ subunits transduce signals affecting expression of soluble second messengers that, in turn, impact the cellular response. B, Phosphorylation of agonist-occupied GPCR by GRK. Free Gβγ subunits mediate recruitment of GRK2 to the plasma membrane into close proximity to activated receptor, prompting the receptor phosphorylation. In addition to Gβγ subunits, GRK2 also binds to plasma membrane-anchored Gαq-GTP and prevents its signaling by sequestration. C, Agonist-bound and GRK-phosphorylated GPCR forms high affinity binding site for βArrestins. The binding of βArrestin to receptor prevents further activation of G proteins and initiates the process of receptor internalization.