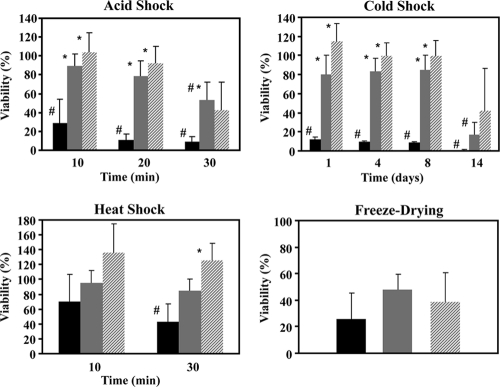
Fig. 5.
Effects of different stresses on the survival of L. lactis strains engineered for trehalose synthesis. Black bars, control strain; gray bars, NZ9000(pNZtpo); dashed bars, NZ9000(pNZotsBA). Viability was calculated as the number of CFU mg protein−1 of cells exposed to stress as a percentage of the number of CFU mg protein−1 of nonstressed cells (for details, see Materials and Methods). For acid stress, cells harvested during the mid-exponential phase were exposed to pH 3.0 (50 mM KPi acidified with HCl) for defined time periods (10, 20, and 30 min). Values are the means of data from at least five independent experiments. For cold stress, survival at 4°C after 1, 4, 8, and 14 days was determined. Values are the means of data from at least four independent experiments. For heat stress, survival was determined upon exposure to 45°C for different time periods. Values are the means of data from at least four independent experiments. For freeze-drying of cells, the rate of survival of cells subjected to one-cycle freeze-drying for 24 h was determined. Values are the means of data from at least five independent experiments. Error bars indicate standard deviations. The asterisk designates statistically significant differences (P < 0.05) between the survival of the engineered strain and that of the control strain. The sharp symbol designates significant differences (P < 0.05) compared to the viability at the 100% level.