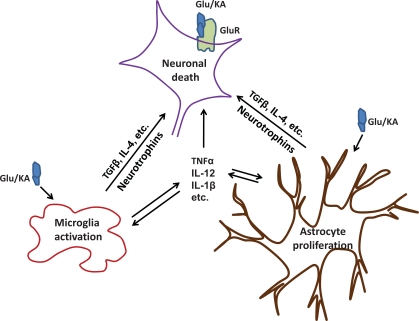
Fig. (6).
Cytokines Involved in Neuron-glia Intercommunication. KA administration enhances further release of endogenous excitatory amino acids, activates microglia and astrocytes. Activated glial cells secrete inflammatory molecules, e.g. cytokines, chemokines, and neurotrophins to influence the outcome of neuronal damage. Glu/KA: glutamate/kainic acid; GluR: glutamate receptors; TGF: transforming growth factor; IL: interleukin; TNF: tumor necrosis factor.