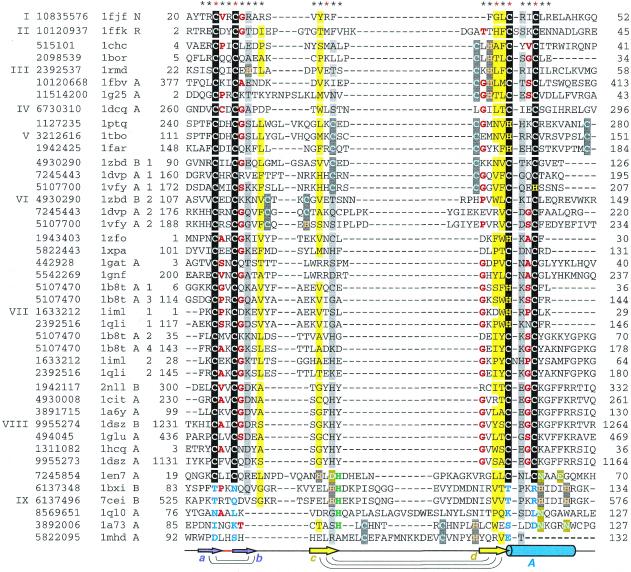
Figure 2.
Structure-based sequence alignment of treble clef fingers. For each sequence, gene identification (gi) number of the NCBI/GenBank protein sequence database, PDB entry name, chain ID (if any), fragment number (if more than one fragment is shown), and starting and ending residue numbers are given. The numbers correspond to the numbering in the PDB file. Sequences are divided into families with the family numbers shown on the left. Families are separated from each other by a larger spacing between the sequences. The families are: I, ribosomal protein L24E; II, ribosomal protein S14; III, RING finger; IV, Pyk2-associated protein β-ARF-GAP domain; V, protein kinase cysteine-rich domain; VI, phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate-binding domain; VII, GATA-1, LIM and DNA repair factor XPA zinc-binding domains; VIII, nuclear receptor DNA-binding domain; IX, His-Me finger endonucleases/MH1 domain of Smad. Zinc ligands in the signature of the treble clef motif are boxed in black, non-zinc-binding residues in corresponding positions are shown in blue, Zn2+ ligands in other sites are boxed in dark gray, Mg2+ ligands are boxed in olive, active site histidine in endonucleases is shown in green, uncharged residues (all amino acids except D,E,K,R) in mostly hydrophobic sites are highlighted in yellow, non-hydrophobic residues (all amino acids except W,F,Y,M,L,I,V) at mostly hydrophilic sites are highlighted in light gray, small residues (G,P,A,S,C,T,V) at positions occupied by mostly small residues are shown in red letters. Secondary structure consensus is shown below the alignment. β-Strands are displayed as arrows, α-helix is shown as a cylinder. Colors and labels are according to the scheme from Figure 1. Arcs connect hydrogen-bonded residues in the β-hairpins. The sites used in r.m.s.d. minimization are marked with asterisks above the alignment. Red asterisks are for the crucial six sites used in the alignment construction.