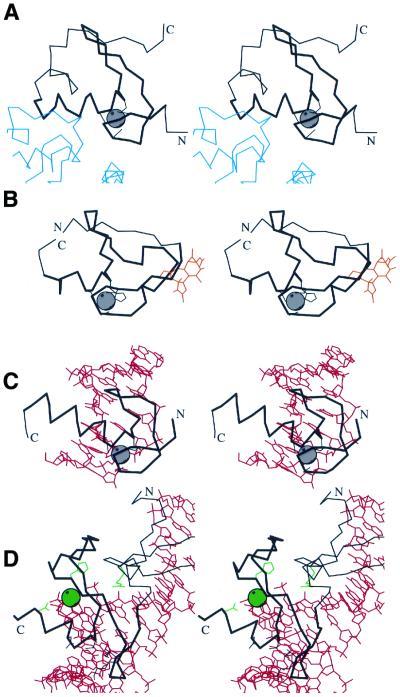
Figure 6.
Functional properties of treble clef fingers. Stereo diagrams of (A) RING finger domain of signal transduction protein Cbl (black) in complex with ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme Ubch7 (blue) (1fbv, chain A, residues 376–431 in black, segments of the chain C in blue); (B) Cys2 activator-binding domain of protein kinase Cδ (black) in complex with phorbol ester (orange) (1ptr, residues 231–280); (C) retinoid X receptor α DNA-binding domain (black) in complex with DNA (red) (2nll, chain B residues 300–336 in black, chains C and D in red); (D) intron-encoded homing endonuclease I-PpoI (black) in complex with DNA (red) (1a73, chain A, residues 49–125 in black, chains C and D in red). Cα traces of treble-clef-containing proteins are displayed in black with N- and C-termini labeled. The treble clef motif is shown in thicker lines. Zinc ions are represented by a gray ball. Side chains of zinc ligands or residues in corresponding sites are shown in black. Side chains of active site residues and an active site Mg2+ ion are shown in green. Cα traces of the polypeptide chains interacting with the treble clef domain are dark blue, small molecules are in orange, DNA chains are in red.