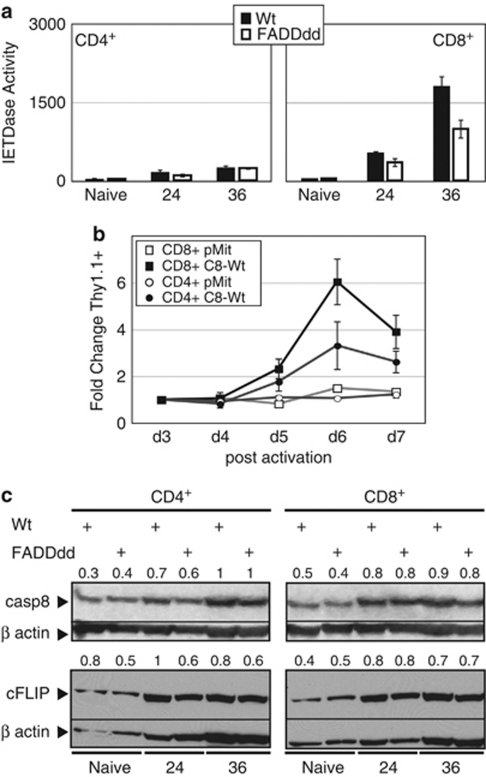
Figure 5.
Differential activation of casp8 in mitogenically stimulated CD8 versus CD4 T cells. (a) CD8+, but not CD4+, T cells exhibit significant IETDase activity after TCR stimulation. CD8+ or CD4+ T-cells subsets from Wt and FADDdd mice were magnetically purified using biotin anti-CD8 or biotin anti-CD4, respectively, and then streptavidin microbeads. After stimulation for the indicated times with anti-CD3 plus anti-CD28, IETDase catalytic activity was measured using the fluorogenic synthetic probe IETD-AFC. Experiments replicated using three mice per genotype; bar charts represent the mean ± S.E.M. (b) Rescue of casp8−/− T cells with wild-type casp8 is greater in the CD8+ subset. CD8+ and CD4+ T cells were stimulated (anti-CD3 plus anti-CD28) and transduced with retroviral supernatants-containing casp8 wild type (C8-Wt) or the empty vector pMit as in Figure 2a. Expression of these vectors was monitored by assessing Thy1.1 expression using flow cytometry. The fold change in Thy1.1 expression from 3 to 7 days relative to day 3 was plotted. Data represent the mean ± S.E.M. of three independent experiments with each vector and each cellular subset. (c) Similar induction of casp8 and c-FLIP expression in CD4+ versus CD8+ T cells. Western blots of naive or activated CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, from either Wt or FADDdd mice, were probed with anti-casp8 or anti-c-FLIP; blots were stripped and reprobed with anti-β-actin as a loading control. Numbers indicate the signal quantification made using ImageJ software. Normalization was performed using β-actin signal