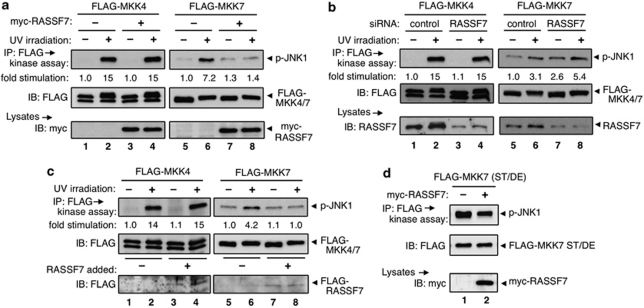
Figure 4.
RASSF7 selectively inhibits UV-induced activation of MKK7. (a) RASSF7 overexpression. HeLa cells were co-transfected with FLAG–MKK4 (lanes 1–4) or FLAG–MKK7 (lanes 5–8), plus myc-mock (−) or myc–RASSF7 (+), and cultured. The cells were exposed to UV (100 J/m2) and cultured for 1 h. Activated MKK4 or MKK7 were precipitated with anti-FLAG beads and subjected to an in vitro kinase assay using GST–JNK1 as a substrate. Lysates and precipitated proteins were immunoblotted to detect the indicated proteins. (b) RASSF7 siRNA. HeLa cells treated with control or RASSF7 siRNA for 24 h, co-transfected with FLAG–MKK4 (lanes 1–4) or FLAG–MKK7 (lanes 5–8) for another 24 h. MKK activity was assessed using the in vitro kinase assay as for a. (c) Addition of RASSF7 protein. HeLa cells transfected with FLAG–MKK4 (lanes 1–4) or FLAG–MKK7 (lanes 5–8), exposed to UV (100 J/m2), and cultured for 1 h. To prepare control or RASSF7 protein, 293T cells were transfected with FLAG-mock or FLAG–RASSF7, and RASSF7 protein was precipitated with anti-FLAG and eluted with FLAG peptide. FLAG–MKK beads were mixed with the FLAG-mock or FLAG–RASSF7 elutants and subjected to in vitro MKK activity assays as for a. (d) Inhibition of constitutively active MKK7. HeLa cells co-transfected with FLAG–MKK7/DE plus myc-mock or myc-RASSF7. MKK7 activity was determined as for a