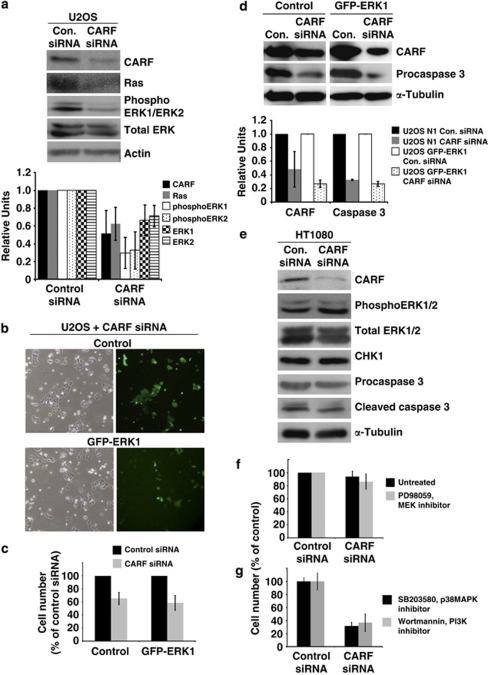
Figure 2.
The Ras-associated pathways are not required for cell death induced by CARF suppression. Ras, total ERK and phosphoERK1/2 were evaluated by immunoblotting in CARF-compromised U2OS cells with densitometric quantitation of representative blots from at least three experiments (a). U2OS cells with overexpression of GFP-ERK1 was transfected with CARF siRNA (b), and cell viability was measured by trypan blue exclusion assay (c) and immunoblotting for procaspase 3 with densitometric quantitation of representative blots from at least three experiments (d). CARF-compromised HT1080 cells were analyzed for total ERK, phosphoERK1/2, CHK1 and caspase cleavage by immunoblotting (e). ERK1/2 was inhibited in CARF-suppressed HT1080 cells by treatment with PD98059, and cell viability was measured using the trypan blue exclusion method (f). p38MAPK and PI3K were inhibited in CARF-compromised U2OS cells by treatment with SB203580 and wortmannin, respectively, and cell viability was measured as above (g). Actin and α-Tubulin were used as loading controls. Densitometric quantitations were performed wherein, the CARF-suppressed group is shown as fold change over control siRNA, which was set as 1. Graphs are represented as average mean±S.D. Cell viability was measured as pecentage of surviving CARF-targeted cells to control siRNA-transfected cells, which was considered as 100%