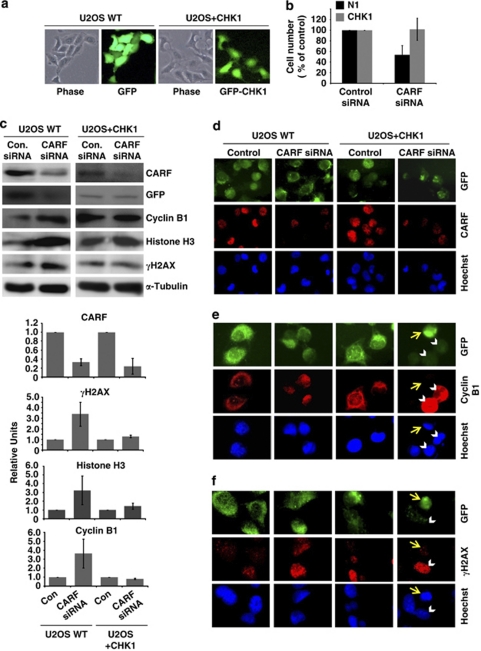
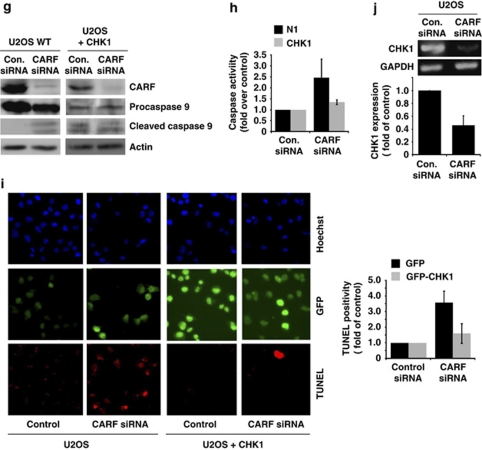
Figure 5.
ATR–CHK1 are required for CARF-suppression-induced cell death. U2OS cells were transiently transfected with GFP-CHK1 or control vector (a). After CARF suppression, cell viability was measured by the trypan blue exclusion method, wherein, the percentage of surviving CARF-targeted cells was compared with control siRNA-transfected cells, which was considered as 100% (b). Immunoblots for CARF, GFP, γH2AX, histone H3 and cyclin B1 were performed in control and CHK-1 overexpressing cells following CARF inhibition with densitometric quantitation of representative blots from at least three experiments, in which the CARF-suppressed group is shown as fold change over control, which was set as 1 (c). Immunofluorescent staining was also performed for CARF, cyclin B1 and γH2AX in methanol/acetone-fixed cells (CARF siRNA-transfected control and CHK1 overexpressing) (d–f). For characterization of the apoptotic phenotype, caspase activation was examined by immunoblotting (g) and fluorescence-based assay (h) in control and CHK1-overexpressing cells following CARF knockdown. Further, TUNEL staining was conducted and quantitated by counting a total of 500–2000 cells from two independent experiments (i). Lastly, using reverse-transcription PCR for CHK1 performed in control and CARF-suppressed cells, we demonstrated that CHK1 transcripts were reduced following CARF knockdown. The PCR products were quantitated from two independent experiments, and the CARF siRNA sample is shown as fold change over control. α-Tubulin was used as loading control and Hoechst 33 258 was used for nuclear staining. Graphs are represented as average mean±S.D.