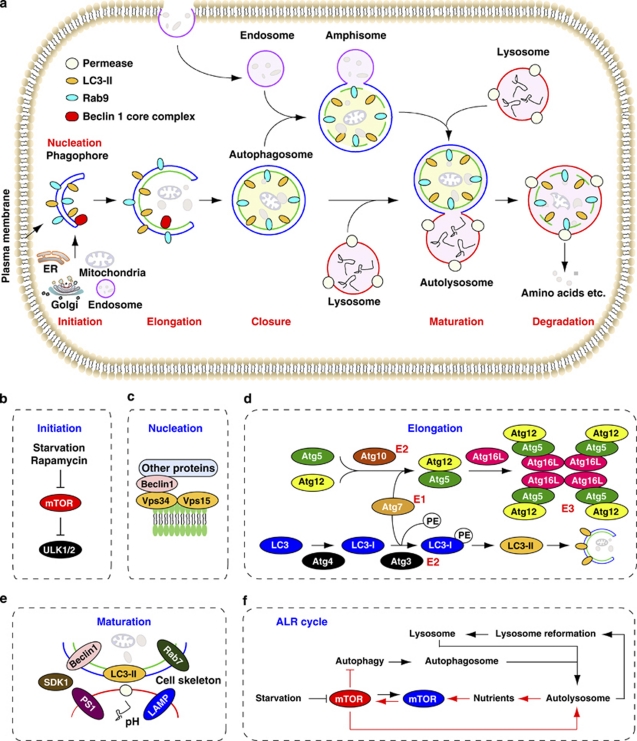
Figure 1.
Stages of autophagy. (a) Different types of autophagy. LC3-II is a marker of Atg5/Atg7-dependent autophagy, whereas Rab-9 is a marker of Atg5/Atg7-independent autophagy. (b) The initiation is sustained by activation of ULK1 and ULK2 complexes, which are inhibited by mTOR. (c) The nucleation depends on Beclin 1-Vps34-Vps15 core complexes and other proteins. (d) The elongation of the phagophore is mediated by two ubiquitin-like conjugation systems that together promote the assembly of the ATG16L complex and the processing of LC3. PE, phosphatidylethanolamine. (e) The maturation is promoted by LC3, Beclin 1, the lysosomal membrane proteins LAMP-1 and LAMP-2, the GTP-binding protein RAB7, the ATPase SKD1, the cell skeleton, the pH of lysosomes and possibly presenilin 1 (PS1). (f) Autophagic lysosome reformation (ALR) cycle. mTOR signaling is inhibited during initiation of autophagy, but reactivated by prolonged starvation. Reactivation of mTOR is autophagy-dependent and requires the degradation of autolysosomal products. Increased mTOR activity attenuates autophagy and generates proto-lysosomal tubules and vesicles that extrude from autolysosomes and ultimately mature into functional lysosomes, thereby restoring the full complement of lysosomes in the cell (figure modified from 1, 6, 73, 74)