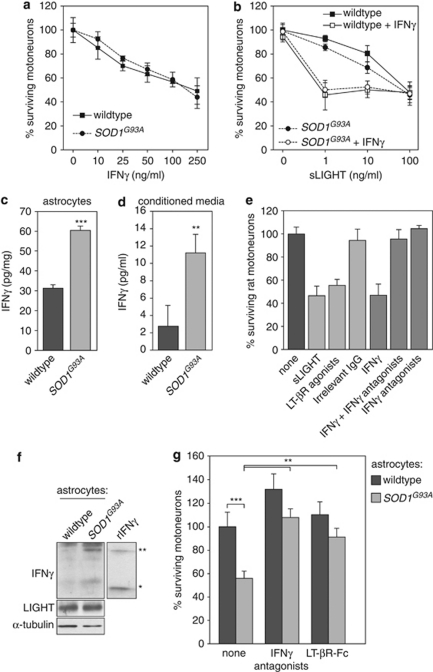
Figure 5.
SOD1 mutant astrocytes kill motoneurons in an IFNγ/LIGHT-dependent pathway. (a) Twenty four hours after plating, indicated concentrations of mouse recombinant IFNγ were added to motoneurons isolated from SOD1G93A or wild-type embryos of the same littermate. Motoneuron survival was determined 48 h later and expressed relative to non-treated condition of corresponding genotype. (b) Mutant SOD1G93A and wild-type motoneurons were treated after 24 h in culture with increasing concentrations of sLIGHT in combination or not with IFNγ (10 ng/ml). Motoneuron survival was determined 48 h after treatment. (c and d) IFNγ levels in extracts (c) and conditioned media (d) of astrocytes of indicated genotype were quantified by ELISA (n=4, means±S.D.). (e) Immunopurified E14 rat motoneurons were treated or not with sLIGHT (100 ng/ml), agonistic anti-LT-βR antibodies (100 ng/ml), irrelevant IgG (100 ng/ml), recombinant soluble rat IFNγ (250 ng/ml) in combination or not with antagonistic anti-IFNγ (500 ng/ml) or anti-IFNγ antibodies alone. Survival of motoneurons was determined 48 h after treatment by direct counting. (f) Total protein extract of wild-type and SOD1G93A rat astrocytes were subjected to sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis followed by immunoblotting with anti-IFNγ specific antibodies. Recombinant rat IFNγ was used as a control. Asterisks indicate the monomeric (*) form of IFNγ and the apparent stable dimeric (**) biologically active form of IFNγ. (g) Wild-type motoneurons were plated on astrocyte monolayer of indicated genotype (wild type, SOD1G93A) and incubated or not with function-blocking anti-IFNγ antibodies (500 ng/ml) or LT-βR-Fc (100 ng/ml) for 48 h. Survival of motoneurons is expressed as the percentage of the number of motoneurons surviving on wild-type astrocyte monolayer in the absence of any treatment. The graphs show the mean values±S.D. of at least three independent experiments performed in triplicate