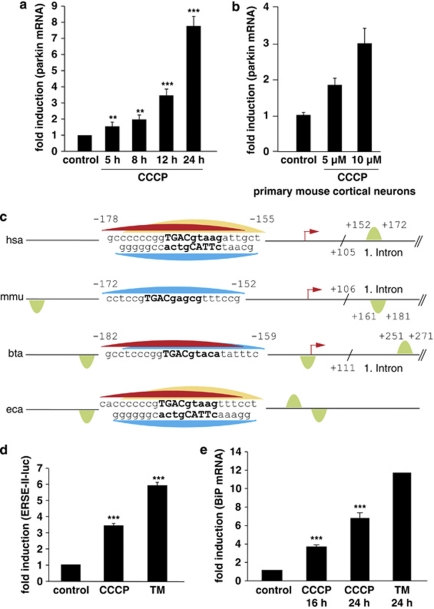
Figure 1.
Mitochondrial stress induced by CCCP activates the UPR and leads to an upregulation of parkin. (a) Parkin mRNA levels are increased in response to mitochondrial membrane dissipation, induced by CCCP. SH-SY5Y cells were incubated with 10 μM CCCP for the indicated time. Cells were collected and total cellular RNA was isolated and subjected to quantitative RT-PCR using parkin-specific primers. The amount of RNA of each sample was normalized with respect to the endogenous housekeeping gene β-actin. Shown is the fold increase of parkin-specific mRNA compared with untreated control cells. (b) Parkin mRNA is upregulated upon CCCP treatment in primary mouse cortical neurons. Primary cortical neurons derived from embryonic mouse brain were incubated with CCCP (10 μM) for 12 h and analyzed as described in (a). (c) Human, mouse, bovine and equine promoter sequences of parkin, which are elongated downstream of the transcription start site (TSS) by 150 bp. Red arrow indicates the TSS and positions are denoted with relative to the TSS. The CREB/ATF-binding sites are indicated by semicircles. Red, yellow and blue semicircles are predicted by three different binding motifs, which correspond to a Genomatix-defined family of 14 matrices describing the CREB/ATF-binding site. The red and yellow colored binding sites are conserved between Homo sapiens, Bos taurus and Equus caballus, and H. sapiens and E. caballus, respectively, whereas the blue binding site is conserved across all four species. The green semicircles (not conserved) are additional binding sites. Downstream of the TSS, in the first intron of the parkin gene, an additional CREB/ATF-binding site is located in H. sapiens, Mus musculus and B. taurus. The consensus ATF4-binding site is written in bold letters. hsa, Homo sapiens; mmu, Mus musculus; bta, Bos taurus; eca, Equus caballus. (d and e) CCCP activates the UPR and causes ER stress. (d) The ER stress luciferase reporter construct ER stress-response element II (ERSE-II-luc) is activated by CCCP. HEK293T cells were transfected with the ERSE-II-luc reporter. At 24 h after transfection, the cells were treated with 10 μM CCCP for 24 h. As a positive control, the cells were treated with the ER stressor tunicamycin (2 μg/ml, 24 h). Shown is the fold induction of luciferase activity in CCCP-treated cells in comparison with non-treated control cells. Quantification is based on triplicates of at least three independent experiments. (e) BiP expression is increased in response to CCCP treatment. As an indicator of ER stress, BiP mRNA levels were analyzed in SH-SY5Y cells treated with CCCP (10 μM) for the indicated time by quantitative RT-PCR as described in Figure 1a. Tunicamycin (2 μg/ml) was used as a positive control to induce ER stress. ***P<0.001, **P<0.01