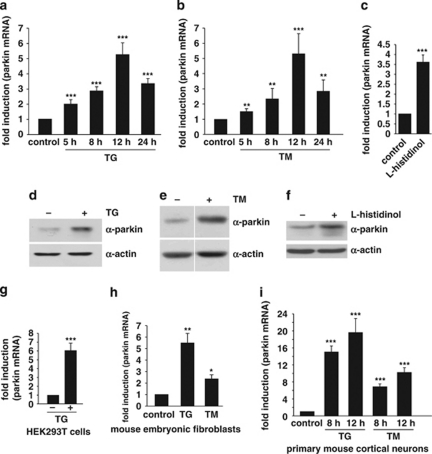
Figure 2.
Parkin gene expression is upregulated in response to ER stress. (a and b) Parkin mRNA levels are increased under ER stress induced by thapsigargin or tunicamycin. SH-SY5Y cells were incubated with 1 μM thapsigargin (TG) (a) or 2 μg/ml tunicamycin (TM) (b) for the indicated time. Cells were collected and total cellular RNA was isolated and subjected to quantitative RT-PCR using parkin-specific primers. The amount of RNA of each sample was normalized with respect to the endogenous housekeeping gene β-actin. The same results were obtained when 18sRNA was used as a control gene (data not shown). Shown is the fold increase of parkin-specific mRNA compared with untreated control cells. (c) Amino acid starvation leads to an upregulation of parkin mRNA. SH-SY5Y cells were treated with 2 mM -histidinol in cell culture medium, containing 10% dialysed FCS, for 14 h. The cells were then collected and total cellular RNA was isolated and subjected to quantitative RT-PCR using parkin-specific primers as described under Figure 1a. (d–f) Parkin protein expression is increased after ER stress induced by TG, TM, or amino acid starvation. Expression of endogenous parkin after treatment of SH-SY5Y cells with TG (d), TM (e) or -histidinol (f) for 14 h was analyzed by western blotting using the anti-parkin mAb PRK8. Loading was controlled by re-probing the blots for β-actin. The western blot image (e) was re-arranged by excluding one line, as indicated by a white line; all samples originate from one gel. (g–i) Parkin mRNA is upregulated on ER stress in HEK293T cells, mouse embryonic fibroblasts and primary mouse cortical neurons. HEK293 T cells (g), mouse embryonic fibroblasts (h), or primary cortical neurons derived from embryonic mouse brain (i) were incubated with TG (1 μM) or TM (2 μg/ml; primary cortical neurons: 3 μg/ml) for 12 or 8 h and 12 h (primary cortical neurons) and analyzed as described in (a). ***P<0.001, **P<0.01, *P<0.05