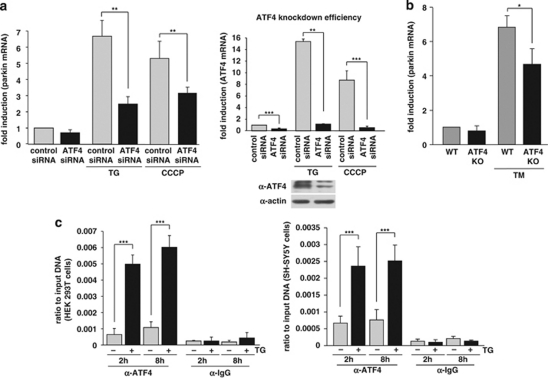
Figure 4.
ATF4 binds to the parkin promoter and mediates parkin upregulation in response to ER and mitochondrial stress. (a) ER and mitochondrial stress-induced upregulation of parkin is impaired in ATF4-deficient cells. SH-SY5Y cells were transfected with ATF4-specific or control siRNA duplexes. Two days later, cells were re-transfected with siRNA duplexes and then incubated with 1 μM TG or 10 μM CCCP for 14 h. The cells were collected and analyzed as described in Figure 1a by quantitative RT-PCR using parkin-specific or ATF4-specific primers. The amount of RNA of each sample was normalized with respect to β-actin. Shown is the fold increase of parkin mRNA in response to TG or CCCP treatment (left panel). The efficiency of ATF4 downregulation was determined by quantitative RT-PCR (right panel) and western blotting (lower right panel) using the anti-ATF4 pAb C-20. (b) ER stress-induced upregulation of parkin is impaired in primary cortical neurons from ATF4-knockout mice. Primary cortical neurons from ATF4-deficient or wild-type mice were treated with tunicamycin (3 μg/ml) for 8 h. Total RNA was isolated and analyzed using parkin-specific primers as described in Figure 1a. (c) ATF4 binds to the parkin promoter in vivo. HEK293T cells or SH-SY5Y cells incubated with or without 300 nM TG for 2 and 8 h were used to perform a ChIP analysis using a pAb specific for ATF4 in comparison with a nonspecific rabbit IgG. For the final real-time PCR step, primers specific for the parkin promoter region were used. ***P<0.001, **P<0.01, *P<0.05