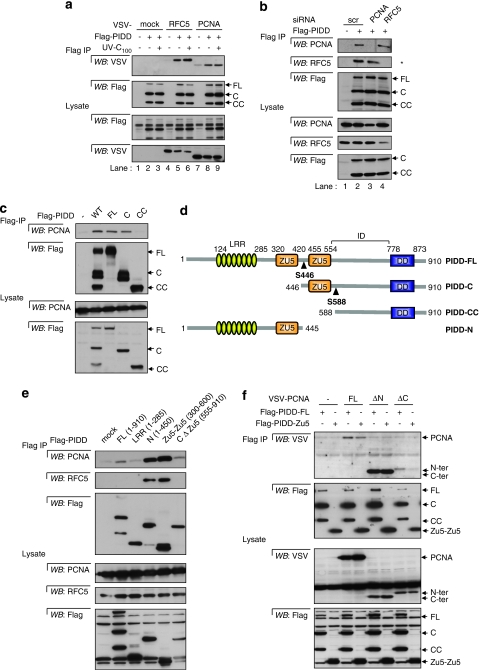
Figure 1.
PIDD interacts with PCNA and RFC5 through its N-terminus. (a) PIDD interacts with overexpressed PCNA and RFC5: different VSV-tagged constructs were cotransfected in 293T cells with Flag-tagged PIDD and tested for interaction by co-immunoprecipitation (after 100 J/m2 UV-C irradiation where indicated). See also Figures S1a and S1b. (b) PIDD interacts with endogenous PCNA and RFC5: scramble or specific siRNAs were cotransfected with Flag-tagged PIDD or a control vector in 293T cells and interactions with endogenous RFC5 and PCNA were analysed by anti-Flag IP (*=a long exposure was required to detect endogenous RFC5). (c) PIDD-CC fragment does not interact with PCNA: 293T cells were transfected with wt or different non-cleavable mutants of PIDD, and endogenous PCNA interactions were analyzed by anti-Flag IP. (d) Structure and processing of PIDD: amino acids positions of each domain are indicated (LRR, Leucine Rich Repeat; ID, Intermediate Domain; DD, Death Domain). (e) Different fragments of PIDD were overexpressed in 293T cells and interactions with endogenous RFC5 and PCNA were analysed by anti-Flag IP. (f) Deletion constructs of PCNA lacking or the C-ter (ΔC=PCNA aa1–120) or the Nter regions (ΔN=PCNA aa130–261), were cotransfected with Flag-tagged PIDD-FL or Zu5-Zu5 in 293T cells and tested for interaction by co-immunoprecipitation. (a–f) All the experiments were repeated at least two times. FL, PIDD Full-length; C, PIDD-C fragment; CC, PIDD-CC fragment as described in panel d (this nomenclature is conserved in all the figures)