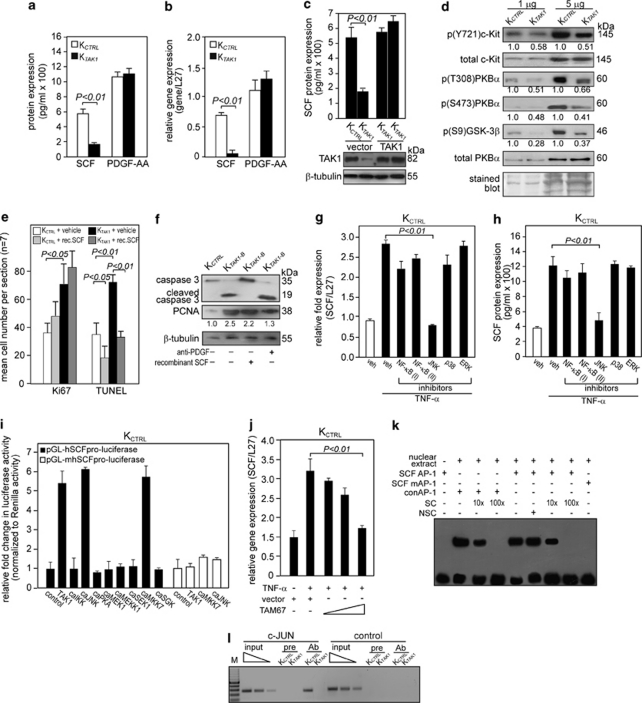
Figure 3.
TAK1 promotes cell survival through the SCF/c-Kit/PKBα pathway. (a and b) Expression level of SCF (a) protein and (b) mRNA in human keratinocytes transduced with either control (KCTRL) or TAK1 siRNA (KTAK1). SCF protein levels were determined from culture medium of KCTRL and KTAK1 by ELISA. Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-AA levels were also measured as a control. Real-time qPCR revealed the relative gene expression of SCF and PDGF-AA in KTAK1 and KCTRL. Ribosomal L27 was used for normalization. Values (mean±S.D.) were from five independent experiments. (c) Expression levels of SCF (upper panel) and TAK1 (lower panel) proteins in KCTRL and KTAK1 transfected with either an empty vector or an expression vector encoding a TAK1 cDNA with a silent third-codon mutation in the siRNA targeting region (upper panel). Two independent transfections are shown. SCF and TAK1 proteins were measured by ELISA and immunoblot, respectively. β-Tubulin was used as a loading and transfer control. (d) Immunoblot analysis of total and phosphorylated c-Kit and its downstream mediators of the PI3K/PKBα pathway in KCTRL and KTAK1 epidermis from OTCs constructed with underlying collagen. The level of p(Y721)c-Kit, the activated form of the SCF receptor, was measured in KCTRL and KTAK1 epidermis. Total c-Kit, PKBα and Coomassie-stained blots were used as loading and transfer controls. (e) Quantification of Ki67 and TUNEL-positive KCTRL and KTAK1 in OTCs supplemented with either vehicle (PBS) as a control or recombinant SCF (rec. SCF). Mean numbers of proliferating and apoptotic cells were numerated after detection by anti-Ki67 antibody or TUNEL, respectively. Values are means from five standardized microscopic fields per section, performed on seven sections from three independent OTCs. (f) Immunodetection of cleaved caspase-3 (apoptotic marker) and PCNA (proliferation marker) in the epithelia from KCTRL- and KTAK1-derived OTCs treated with either PBS (−), anti-PDGF antibody or recombinant SCF (+). β-Tubulin served as a transfer and loading control. Values below each band represent the mean fold differences (n=3) in expression level compared with KCTRL, which was assigned the value of 1. (g and h) TAK1 regulates SCF expression via MKK7/JNK/c-Jun pathway. Expression level of SCF (g) mRNA and (h) protein in KCTRL treated with either DMSO (vehicle control) or specific inhibitors of the indicated kinases in the presence of TNF-α (10 ng/ml). The various kinase inhibitors were NF-κB (I): BAY 11-7082; NF-κB (II): SN50; JNK: 1,9-pyrazoloanthrone; p38: (2-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-pyridin-4-yl-1,2-dihydropyrazol-3-one); and ERK1/2: PD98059. Ribosomal L27 was used for normalization in qPCR. Protein levels were determined by ELISA. (i) Transactivation assay in keratinocytes co-transfected with a luciferase reporter gene driven by the human SCF promoter (pGL-hSCFpro-luciferase), cDNA encoding for indicated constitutively active (ca) kinases and pEF1-β-galactosidase as control for transfection efficiency. Luciferase activity was measured, and normalized reporter activity is shown as fold induction compared with reporter construct-transfected KCTRL (control). The SCF promoter reporter construct with a mutated AP-1 site is denoted pGL-mSCFpro-luciferase. Values (mean±S.D.) are from three independent experiments. (j) Relative SCF mRNA expression in KCTRL transfected with increasing amount of dominant-negative c-Jun (TAM67). Ribosomal L27 was used for normalization. (k) EMSA of the human SCF AP-1-binding site. Biotin-labeled SCF AP-1 binding sequence was incubated with nuclear extract isolated from KCTRL. NSC denotes non-specific competitor, a scrambled AP-1-binding sequence. SC denotes non-labeled consensus AP-1 sequence (conAP-1). As positive control, conAP-1 was used. Mutated SCF AP-1 site is denoted as SCF mAP-1. (l) Human SCF is a direct AP-1 target gene. Chromatin immunoprecipitation was done in KCTRL and KTAK1 using pre-immune IgG (pre) or antibody against phospho-c-Jun (Ab). The promoter region with the AP-1-binding site was immunoprecipitated and specifically amplified in KCTRL using Ab. No amplified signal was obtained in KTAK1 or using pre-immune IgG (pre). A control region upstream of the AP-1-binding site served as a negative control. M: 100-bp DNA marker