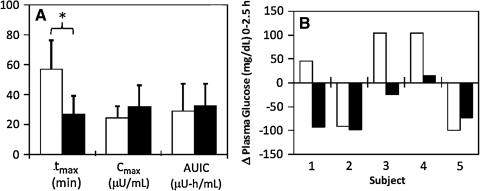
FIG. 3.
Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic parameters of the 9-mm catheter (open columns) and 900-μm-long microneedle (solid columns). (A) Pharmacokinetic parameters time to peak insulin concentration (tmax), peak insulin concentration (Cmax), and area under the insulin curve (AUIC) for subcutaneous catheter and intradermal microneedle treatments. The average tmax value for the intradermal microneedle was significantly smaller than that for the subcutaneous catheter control, indicating rapid absorption of insulin. The AUICs were similar, indicating comparable relative bioavailability. *P < 0.05. (B) Comparison of the net change in plasma glucose levels between the two treatment methods for each of the five subjects 2.5 h after insulin administration. Overall, intradermal microneedle injection was more effective than subcutaneous catheter infusion in reducing plasma glucose levels either to or below baseline glucose levels.