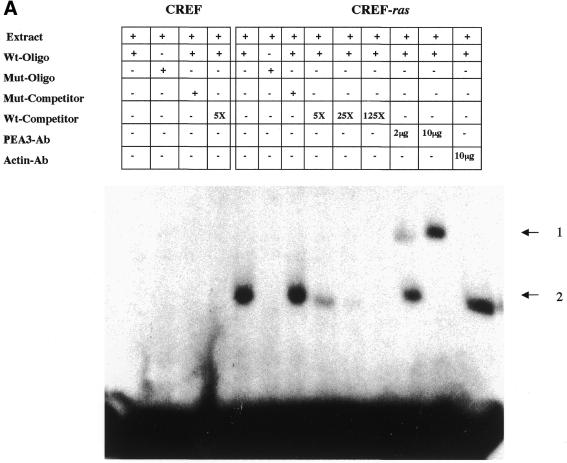
Figure 9.
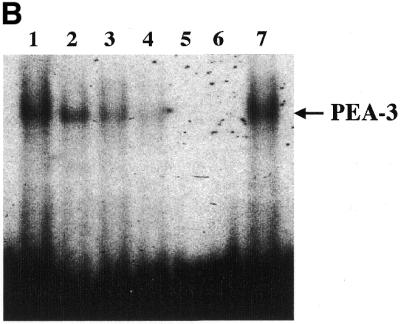
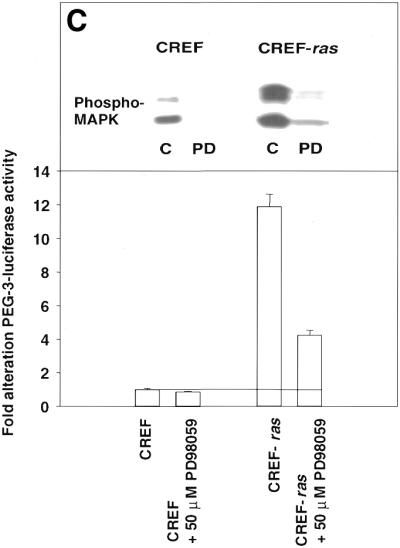
Analysis of nuclear protein binding to PEA3 elements by EMSA and inhibition of binding and PEG-Prom activity by MAPK inhibition. (A) PEA3 nucleoprotein complexes in CREF and CREF-ras cells were identified using EMSA. Nuclear extracts were prepared from the two cell types and incubated with a PEA3 probe with the sequence 5′-GTGTTGTTTTCCTCTCTCCA-3′/3′-CACAACAAAAGGAGAGAGGT-5′ (extending from nucleotides –112 to –93) labeled using [γ-32P]ATP and T4 DNA kinase. The reaction mixture was electrophoresed in a 5% non-denatured polyacrylamide gel as described in Materials and Methods. Arrow 1 indicates the supershifted PEA3 DNA–protein complex in CREF-ras cells. All of the samples contain nuclear extracts from either CREF or CREF-ras cells. Mut-oligo samples contain a mutated PEA3 oligonucleotide with the sequence 5′-GTGTTGTTCCCATCTCTCCA-3′/3′-CACAACAAGGGTAGAGAGGT-5′. Wt-oligo sample contains a wild-type PEA3 oligonucleotide. Mut-Competitor refers to the presence of a 125-fold molar excess of unlabeled mutant oligonucleotide. Wt-Competitor refers to the presence of a 5-, 25- or 125-fold molar excess of unlabeled wild-type competitor. PEA3-Ab samples contain 2 or 10 µg of anti-PEA3-Ab. Actin-Ab sample contains 10 µg of anti-actin antibody. (B) Effect of MAPK inhibition on PEA3 binding in CREF-ras cells. Nuclear extracts were prepared from cells either untreated or treated for 6 h with PD98059 (50 µM) and EMSA performed as described in (A). Lane 1, DMSO (0.05%) (control); lane 2, 50 µM PD98059; lane 3, 100 µM PD98059; lane 4, 150 µM PD98059; lane 5, control lacking nuclear protein, only containing labeled probe; lane 6, competition sample containing nuclear protein, labeled probe and 100× unlabeled PEA3 competitor probe; lane 7, positive sample containing nuclear protein and labeled probe. (C) Inhibition of MAPK reduces PEG-3 promoter function in CREF and CREF-ras cells. CREF and CREF-ras cells were transfected with a FL-PEG-Prom. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were treated with either vehicle control (VEH) or the MEK1/2 inhibitor PD98059 (50 µM). Two hours after treatment, cells were harvested and, in parallel, the activity of the FL-PEG-Prom was determined as in Materials and Methods, and MAPK activity was determined by use of a phospho-specific antibody (inset panel).