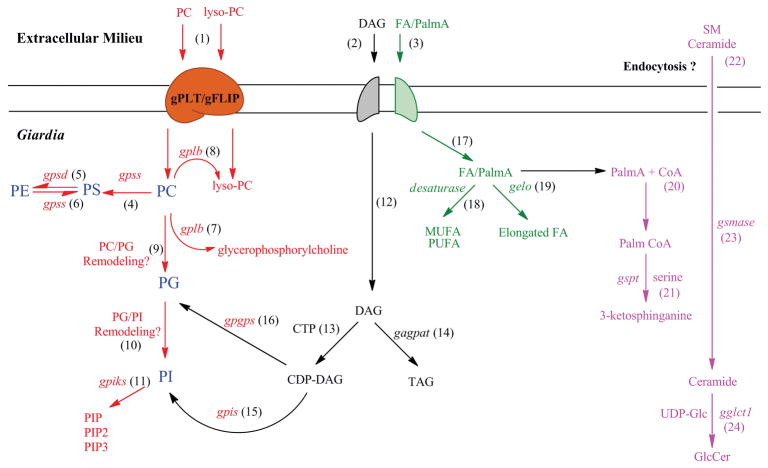
Fig. 4.
Proposed lipid metabolic pathways in Giardia. The model proposes that PC and lyso-PC, which are abundant in the growth medium, can be taken up by Giardia with the help of gPLT or gFLIP (step 1). Diacylglycerol (DAG) and FA are internalised by specific transporter(s) from the growth medium (steps 2 & 3). Internalised PC can be converted to PS with the help of gPSS1-like enzyme encoded by putative gpss gene (step 4). Giardia expresses psd gene (Yichoy et al. 2009), and its possible encoded product (gPSD) may facilitate PE synthesis from PS (step 5). The putative gpss can also encode gPSS2-like enzyme for the synthesis of PS from PE (step 6). Because PG is the major phospholipid in Giardia and is not present in the growth media (Yichoy et al. 2009), it is likely that Giardia has the ability to synthesize PG not only by CDP-DAG pathway (step 16) but also by the headgroup remodelling reaction shown in step 9. Similarly, PI is synthesized from PC by base or headgroup exchange reactions from PG (step 10). However, the presence of these two pathways—i.e., PC -> PG and PG -> PI—is yet to be elucidated in Giardia or other eukaryotic cells. PI can be converted to various phosphinositides facilitated by gpiks (step 11) as mentioned before (Cox et al. 2006; Hernandez et al. 2007b). Giardial plb and lpl gene may be responsible for synthesizing glycerophosphorylcholine from PC and lyso-PC, respectively (steps 7 & 8). Diacylglycerol (DAG) obtained from the growth medium can be converted to CDP-DAG (step 13) and serves as a precursor for TAG (step 14), PG (step 15), and PI (step 16). Exogenous FAs can produce unsaturated FAs (MUFA and PUFA) and elongated FAs as depicted in steps 18 & 19. Exogenous PalmA can be used as a precursor to synthesize 3-ketosphinganine with the help of gspts (steps 20–21). Similarly, both ceramide and SM can be acquired from the growth medium (step 22) by endocytic and non-endocytic pathways. Exogenously obtained SM can be hydrolyzed by gsmases to produce ceramide (step 23), and ceramide can be used to synthesize GlcCer (step 24). PC, phosphatidylcholine; lyso-PC, lyso-phosphatidylcholine; PS, phosphatidylserine; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PIP, phosphatidylinositol phosphate; PIP2, phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate; PIP3, phosphatidylinositol triphosphate; DAG, diacylglycerol; TAG, triacylglycerol; CTP, cytidine triphosphate; FA, fatty acid; MUFA, monounsaturated fatty acid; PUFA, polyunsaturated fatty acid; SM, sphingomyelin; GlcCer, glucosylceramide. For better understanding, phospholipid pathways are shown in red, neutral lipids (DAG and TAG) in black, FAs in green, and SLs in pink.