Fig. 1.
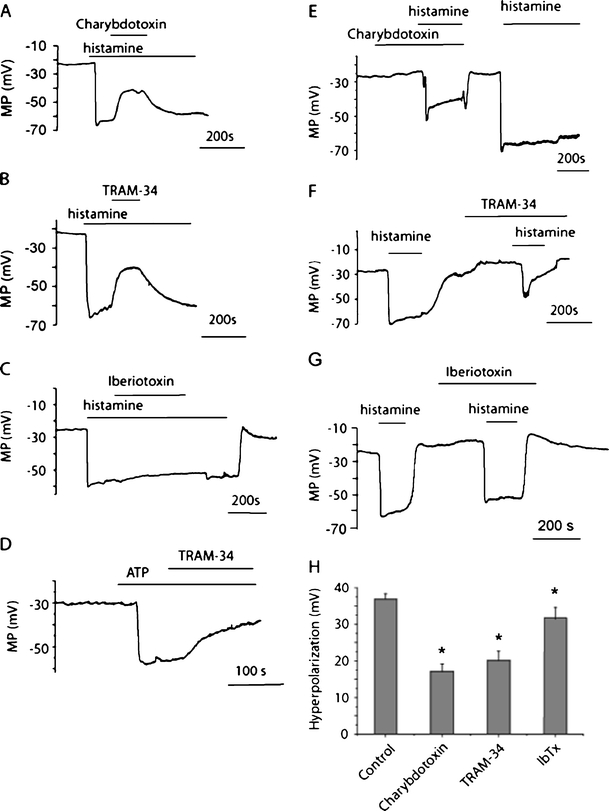
Effect of IKCa channel inhibitors on endothelial hyperpolarization. a Typical membrane potential recording showing the effect of charybdotoxin (100 nM) applied during the plateau phase of hyperpolarization to 10 μM histamine. b Typical membrane potential recording showing the effect of TRAM-34 (2 μM) applied during the plateau phase of hyperpolarization to 10 μM histamine. c Typical membrane potential recording showing the effect of iberiotoxin (200 nM) applied during the plateau phase of hyperpolarization to 10 μM histamine. d Typical membrane potential recording showing the effect of TRAM-34 (2 μM) applied during the plateau phase of hyperpolarization to 10 μM ATP. e Typical membrane potential recording showing the effect of preexposure to charybdotoxin (100 nM) on hyperpolarization to 10 μM histamine. f Typical membrane potential recording showing the effect of preexposure to TRAM-34 (2 μM) on hyperpolarization to 10 μM histamine. g Typical membrane potential recording showing the effect of preexposure to iberiotoxin (200 nM) on hyperpolarization to 10 μM histamine. h Statistical representation of the effect of charybdotoxin (100 nM; n = 4), TRAM-34 (2 μM; n = 5) and iberiotoxin (200 nM; n = 5) on peak hyperpolarization to 10 μM histamine (n = 11). *P < 0.05 vs control hyperpolarization
