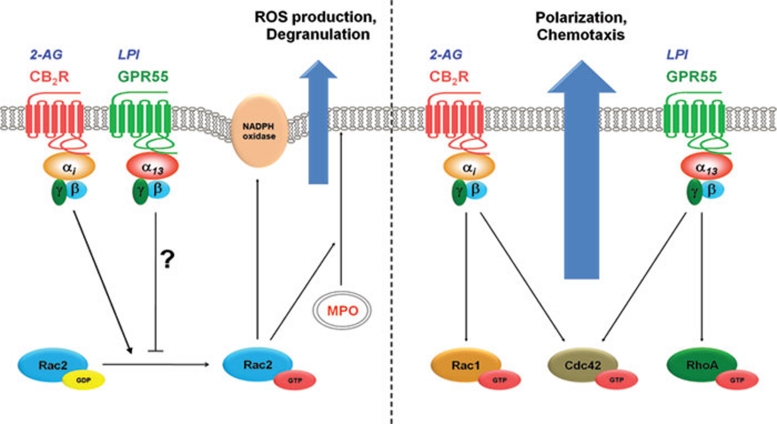
Figure 7.
Crosstalk between GPR55 and CB2R and its consequent biological responses in human blood neutrophils. (right panel) Stimulation of CB2R and GPR55 by 2-AG and LPI, respectively, leads to a coordinated activation of RhoA, Rac1 and Cdc42 small GTPases. This leads to a distinct remodeling of cytoskeleton (polarization) compared to sole activation of each receptor and facilitates neutrophils migration towards the gradient of agonists. (left panel) The bacterial killing mechanisms, which are provoked by C5a or 2-AG, are mediated via the activation of Rac2 small GTPases. Active Rac2 will translocate and incorporate to the NADPH oxidase core complex in the phagocytic cup and catalyzes the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). On the other hand, it facilitates degranulation of neutrophils via translocation of azurophilic granules, containing myeloperoxidase (MPO). Stimulation of GPR55 by LPI, via a yet unknown mechanism, inhibits activation of Rac2, thereby limiting the ROS production and degranulation.