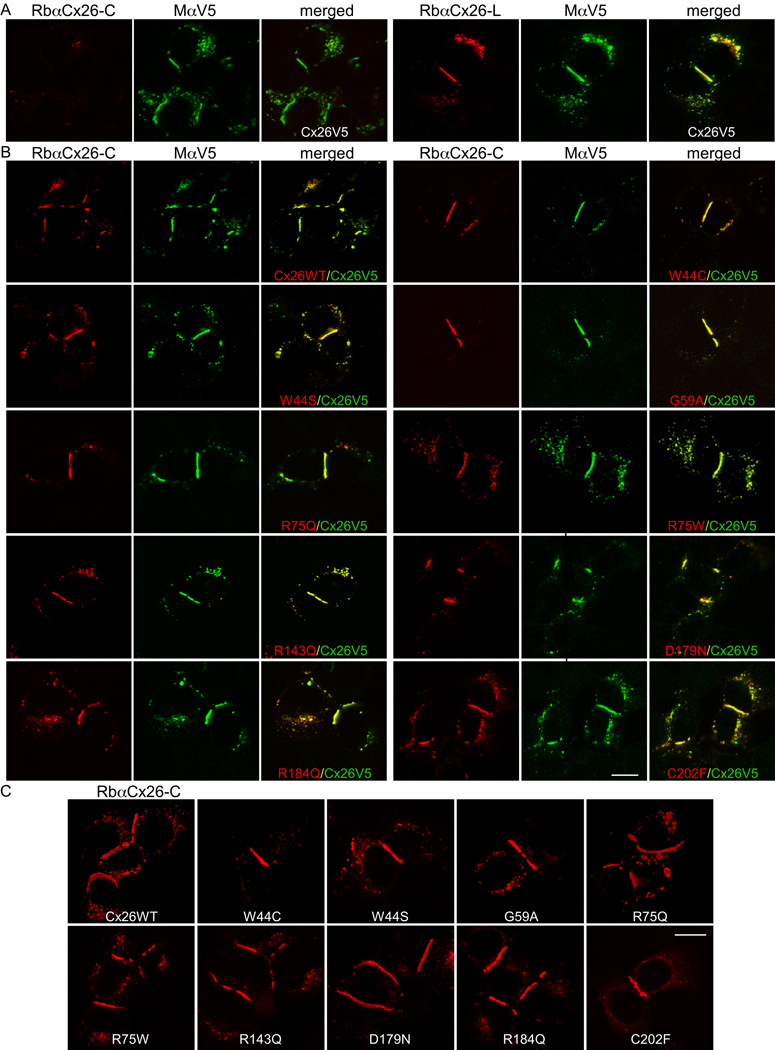
Figure 1. Dominant Cx26 mutants co-localize with WT Cx26 at gap junction plaques.
These are confocal images of transiently transfected HeLa cells that express WT Cx26 with a C-terminal V5 epitope tag (Cx26V5) alone (A), or co-express Cx26V5 and WT Cx26 (Cx26WT) or the indicated Cx26 mutants (B), or the individual Cx26 mutants alone as indicated (C) (A) These cells were co-labeled with a mouse antibody against V5 (MaV5) and a rabbit antiserum against the C-terminus (RbaCx26-C, left panel) or the cytoplasmic loop (RbaCx26-L, right panel) of Cx26. Note that the V5 tag did not alter the trafficking of Cx26V5 to gap junction plaques at apposed cell borders as visualized with MaV5 or RbaCx26-L (right panel), whereas the immunoreactivity to the RbaCx26-C was minimal and never seen at the gap junction plaques (left panel), indicating that the V5 tag prevented the binding of the RbaCx26-C antiserum.
(B) These cells were co-labeled with RbaCx26-C (to visualize the untagged WT or mutant Cx26) and MaV5 (to visualize Cx26V5). Similar to Cx26WT, all of these Cx26 mutants were colocalized with Cx26V5, including at gap junction plaques. Scale bar: 10 µm. (C) These are confocal images of HeLa cells transiently transfected to express WT Cx26 (Cx26WT) or the indicated Cx26 mutants. The cells were labeled with a rabbit antiserum against the C-terminus of Cx26. Similar to the WT Cx26, all of these mutants formed gap junction plaques at apposed cell borders. Scale bar: 10 µm.