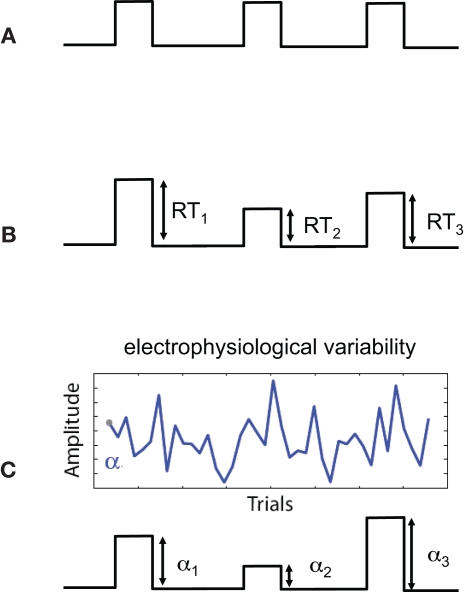
Figure 1.
Sources of uncertainty in different regressor models. Shown are three regressor types (before convolution with the hemodynamic response function). (A) Regressor constructed from the onset times of the stimulus. The high certainty in this type of regressor is a result of stimulus times being set by the experiment and measured exactly. There is no uncertainty in the interpretation of amplitudes since they are constant. (B) Regressor constructed by modulating the stimulus onset times by response times (RTs). Measurement noise of RTs is low (i.e., RTs are high SNR measurements) however there is additional uncertainty (relative to case A) in terms of the interpretation of the trial-by-trial variations in response time. (C) Regressor constructed by modulating stimulus by activity derived from electrophysiological variability. Sources of uncertainty include both measurement noise, due to the low SNR of the signal, as well as the interpretation of the trial-to-trial electrophysiological variability.