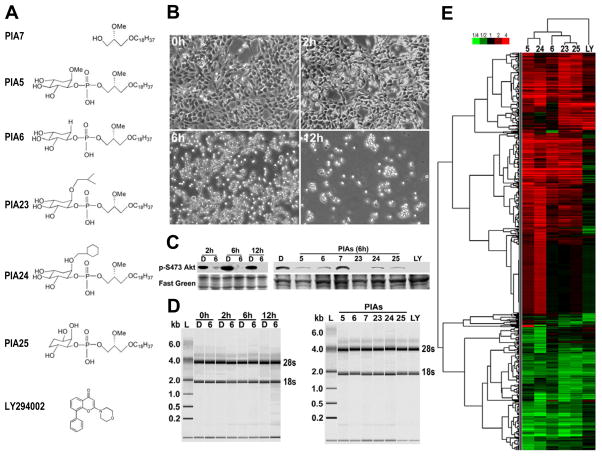
Figure 1.
Optimization of PIA treatment and oligonucleotide microarray analysis. A) The chemical structures of the inactive PIA7, 5 active PIAs and PI3K inhibitor LY294002. B) Cellular morphological alterations induced by PIA treatment. H157 cells were incubated with 10 μM PIA6 dissolved in DMSO in RPMI1640 + 0.1% FBS media for the indicated times. C) Evaluation of Akt inhibition in samples collected for microarray analysis. Parallel H157 cell samples were collected for analysis of p-S473 Akt by immunoblot, alongside microarray samples for RNA extraction, in time course and PIA comparison experiments as described in Materials and Methods. D = DMSO, 5, 6, 7, 23, 24, 25 = 10 μM PIA-treated samples, LY = 10 μM LY294002-treated sample. D) Assessment of RNA quality and integrity in microarray samples using the Bioanalyzer Nanochip. Prominent bands indicate positions of 28s and 18s rRNA. E) Clustered heat map showing PIA-altered genes. Red color = induction, green color = suppression, black color = no change in expression. Complete linkage hierarchical clustering of PIA-regulated gene expression changes in H157 cells was performed with uncentered correlation as described in Materials and Methods.