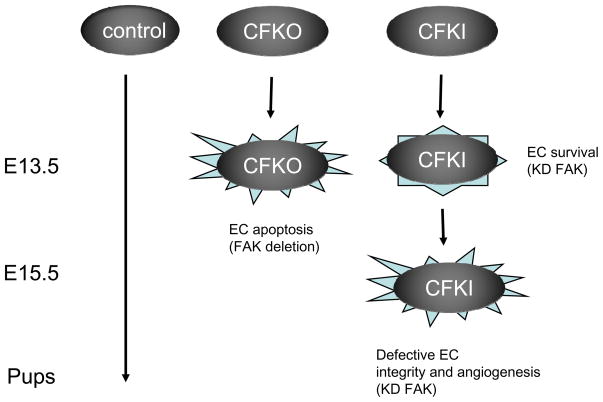
Fig. 3. A working model of kinase-dependent and -independent functions of FAK in vascular development.
In control embryos, normal FAK functions in ECs allow completion of embryonic development. In FAK conditional knockout (CFKO) embryos, absence of FAK leads to EC apoptosis and embryonic lethality at E13.5. In EC-specific FAK kinase-defective mutant knockin (CFKI) embryos, the kinase-independent functions of FAK support EC survival to allow development beyond E13.5. However, lack of FAK kinase activity results in other defects in EC junctions and angiogenesis, leading to embryonic lethality at E15.5.