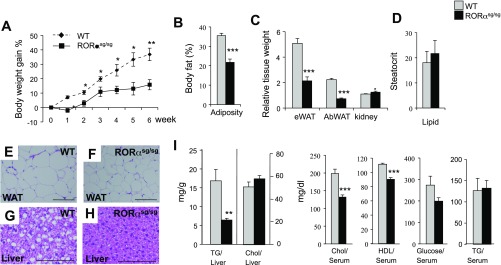
Fig. 2.
RORαsg/sg mice are resistant to diet-induced obesity and hepatic steatosis. A: 10 wk old male mice (WT, n = 6; RORαsg/sg, n = 7) were fed a high-fat diet (HFD) for 6 wk, and weight gain was monitored. The percent body weight gain was calculated based on the body weight at the start of the HFD. B: total body fat mass was analyzed by Piximus densitometry. C: comparison of the relative weights of kidneys, epididymal white adipose tissue (eWAT), and abdominal WAT (AbWAT) after 6 wk on an HFD. D: comparison of the steatocrit in feces of WT(HFD) and RORαsg/sg(HFD) male mice (WT, n = 5; RORαsg/sg, n = 6). E–H: representative H&E-stained sections of liver and WAT from WT(HFD) and RORαsg/sg(HFD) male mice. Scale bar indicates 200 μm. I: comparison of hepatic triglyceride (TG) and cholesterol (Chol) levels, and serum Chol, HDL, glucose, and TG levels in WT(HFD) and RORαsg/sg(HFD). Data present means ± SE; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.