Fig. 4.
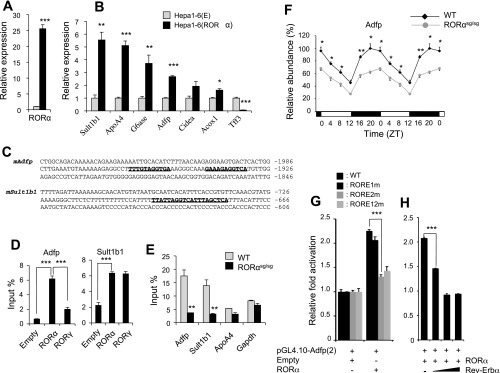
Several RORα-responsive genes are regulated directly by RORα. A: comparison of RORα mRNA expression in Hepa1–6(E) and Hepa1–6(RORα) cells stably expressing empty vector or RORα, respectively. B: increased expression of several RORα-responsive genes in Hepa1–6(RORα) compared with Hepa1–6(E) cells. Expression was analyzed by QRT-PCR. C: identification of 2 putative ROREs (boldfaced and underlined) in the promoter of Adfp and Sul1b1 genes. RORα is associated with RORE-containing regulatory regions of the Adfp and Sult1b1 genes. ChIP analysis was performed with Hepa1–6(E), Hepa1–6(RORα), or hepa1–6(RORγ) using anti-Flag M2 antibody (D) or with liver from WT or RORαsg/sg mice using an RORα antibody as described in materials and methods (E). F: the expression of Adfp was examined in liver of WT and RORαsg/sg mice during the circadian time. At each time point 4 mice for each group were analyzed. G: RORα increased Adfp proximal promoter activity through RORE2. Hepatoma Huh-7 cells were cotransfected with pCMVβ-Gal, 3xFlag-CMV10-RORα4 or empty vector, and pGL4.10-Adfp(2) or the reporter plasmid in which RORE1, RORE2, or both (RORE1/2m) were mutated as indicated. The relative luciferase reporter activity was determined 48 h later. H: Rev-Erbα inhibited the enhanced activation of the Adfp promoter by RORα. Cells were cotransfected with 3xFlag-CMV10-RORα4 and pGL4.10-Adfp(2) and 3xFlag-CMV10-Rev-Erbα as indicated and processed as in G. Data present means ± SE. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.