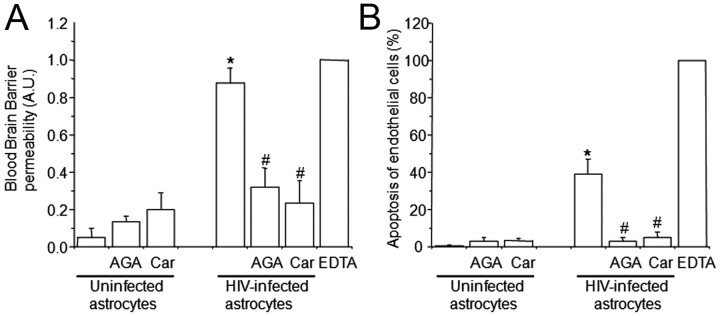
Figure 2.
The use of HIV-infected astrocyte cultures to establish the human BBB model results in BBB permeability (A) and endothelial apoptosis (B). BBB disruption was evaluated by the permeability of the model to albumin conjugated to Evans blue dye, and endothelial apoptosis was evaluated by TUNEL. A, BBB models using uninfected astrocytes were totally impermeable to albumin conjugated to Evans blue dye. Gap junction blockers AGA or Car did not alter BBB integrity when uninfected astrocytes cultures were used to establish the model. The BBB established using HIVADA-infected astrocyte cultures had disrupted integrity, despite no detectable infection of astrocyte cultures as assayed by p24 ELISA. Addition of gap junction blockers AGA (32 μm) or Car (10 μm) in the bottom chamber on the BBB model (astrocyte side) inhibited BBB disruption. EDTA added to the BBB model was used as a positive control for disruption (n = 4; *p ≤ 0.005 compared with control conditions using uninfected astrocytes; #p ≤ 0.005 compared with the BBB model using HIV-infected astrocytes). B, Determination of endothelial apoptosis using TUNEL staining and confocal microscopy of control BBB cultures indicated no apoptosis. Gap junction blockers AGA or Car, used in treating control BBB cultures established with uninfected astrocytes, did not cause endothelial apoptosis. BBB models with HIVADA-infected astrocyte cultures exhibit significantly increased endothelial apoptosis. Addition of GJ blockers AGA or Car (10 μm) in the bottom chamber of the BBB model (astrocyte side) totally abolished endothelial apoptosis induced by few HIV-infected astrocytes (n = 4; *p ≤ 0.005 compared with control conditions; #p ≤ 0.005 compared with BBB using HIV-infected astrocytes).