Figure 2. Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometric Analysis of Extracts of Murine White Adipose Tissue by MDMS-SL.
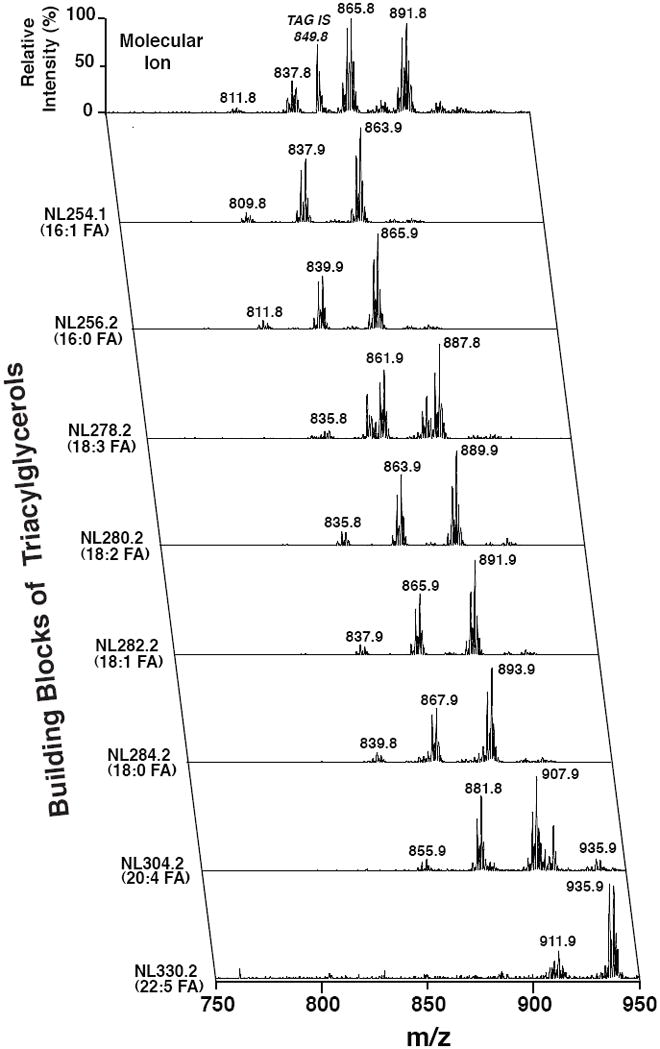
Bligh and Dyer extracts of white adipose tissue from mice fed a high fat diet were prepared as previously described (Han and Gross, 2005) and directly infused into the ESI ion source. Positive-ion ESI mass spectra identified multiple molecular ions in the full mass scan (top row; x-axis) that were quantitated through ratiometric comparisons with internal standard (tri 17:1 triacylglycerol, m/z 849.8) after corrections for isotope abundance and acyl chain length and unsaturation effects. Tandem mass spectrometric analysis was performed using neutral loss scanning for the indicated naturally occurring aliphatic chains. All scans were normalized to the base peak of the individual spectrum. Through bioinformatic analysis of the ion counts in each row (x-axis scan) and column (y-axis scans), the compositional identities of each individual molecular species can be determined and their relative abundance can be quantified.
