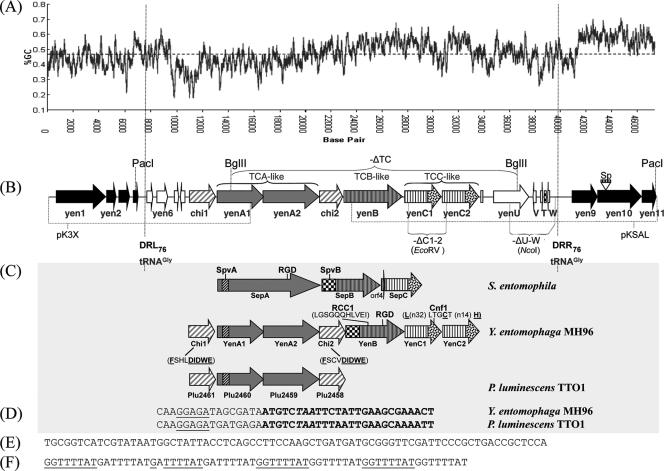
Fig. 1.
(A) G+C content of PAIYe96 and the associated genomic region (window size 300, window position shift). (B) Schematic of Y. entomophaga MH96 PAIYe96. Black arrows denote Y. entomophaga MH96 genomic DNA. The locations and designations of the PAIYe96 virulence determinants as defined in Table 2 are shown. The location of the SphI genomically integrated spectinomycin resistance cassette (Sp) to form Y. entomophaga MH96Sp is shown (Table 1; see text); the PacI restriction enzyme sites used to clone the region associated with the virulence genes are indicated. The BglII, EcoRV, and NcoI restriction enzyme sites used to delete the virulence gene-associated region in the ΔTC mutant strain and associated yenC1-yenC2 (-ΔC1-2) and yenUVTW (-ΔU-W) ORFs, respectively, are depicted (see text). The pKSAL and pKX3 sequencing clones (Table 1) are indicated. (C) Similarity of the toxin complex (TC) YenA1 and YenA2-chitinase associated region to its closest orthologues of P. luminescens TTO1 (Table 2) and comparison of the relative size of the YenA1 and YenA2 proteins to the toxin complex A (TCA) S. entomophila SepA orthologue. Regions of amino acid similarity to SpvA and SpvB are indicated. Predicted protein domains: YenA1 (SpvA, amino acids [aa] 56 to 185); YenB, (SpvB, aa 9 to 366; RCC1, aa 572 to 582; RGD, aa 836 to 838); Chi1 (Chi 18 hydrolytic site, aa 248 to 256); Chi2 (Chi 18 hydrolytic site, aa 431 to 349); YenC1 (necrotizing factor Cnf1, aa 815 to 819, and its associated Rho-activating domain and catalytic triad [10] [underlined] is indicated). The vertical lines denote the conserved amino terminus and the stippling in the arrows indicates the variable carboxyl region of the TCC-like Rhs elements (33). (D) Nucleotide sequence of the Y. entomophaga MH96 (yenA1-yenA2) and P. luminescens TTO1 (plu2460-plu2459) translational coupling DNA sequence. The termination codon of yenA1 or plu2460 is shown in italic type. The 5′ end of the yenA2 or plu2459 ORF is shown in bold type. The predicted yenA2 or plu2459 ribosomal binding site is underlined. (E) tRNAGly 76-bp direct repeats (DRL76 and DRR76). (F) Nucleotide sequence of the eight-copy 8-bp repeat located upstream of yenU.