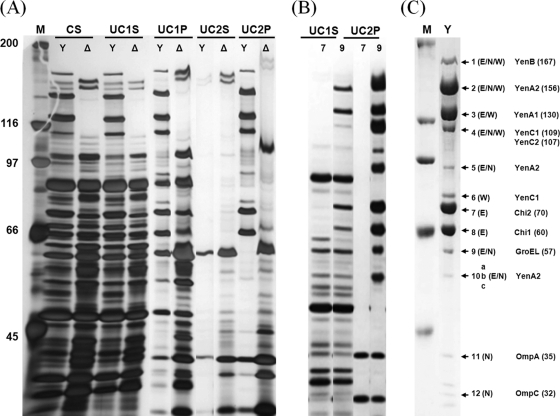
Fig. 4.
(A) Silver-stained SDS-polyacrylamide gel of Y. entomophaga MH96 and ΔTC mutant strain. Y. entomophaga MH96 (Y) and ΔTC mutant strain (Δ) in culture supernatant (CS), ultracentrifuged supernatant (UC1S), ultracentrifuged pellet (UC1P), supernatant after ultracentrifugation and application to a step gradient (UC2S), and pellet after ultracentrifugation and application to a step gradient (UC2P). (B) Silver-stained SDS-polyacrylamide gel of Y. entomophaga MH96::7 (7) and Y. entomophaga MH96::9 (9), showing the absence of formation of the complex and a complex missing the YenB component, respectively. (C) SDS-polyacrylamide gel stained with Coomassie brilliant blue showing bands assessed by either LC-ESI-MS/MS (E), N-terminal sequence analysis (N) (Table 8), or Western immunoblot (W). The M lanes contain Bio-Rad broad-range markers. The positions of molecular mass markers (in kilodaltons) are indicated to the left of the gel. The locations of components of the TC, GroEL, OmpA, and OmpC proteins are indicated (Table 8; see text; also see Table S2 in the supplemental material).