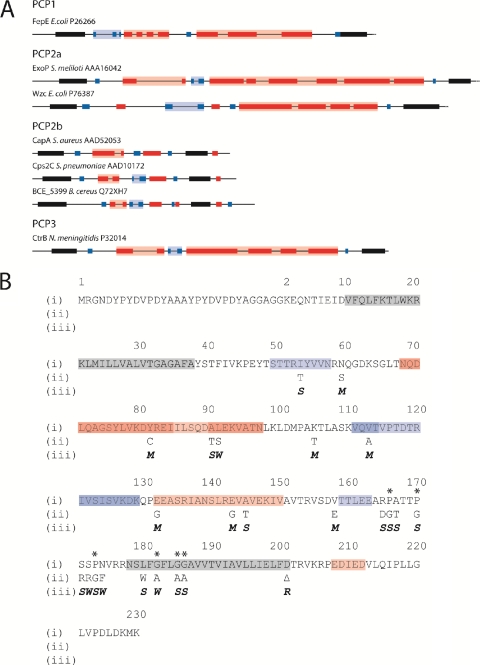
Fig. 1.
Predicted secondary structures of selected PCP2 proteins. (A) Complete open reading frames of selected PCP2 proteins were submitted to the Predict Protein server (http://www.predictprotein.org/), and the outputs from the programs PHDhtm (Predict transmembrane) and PROF (Predict secondary structure) were used to predict TM regions and secondary-structure features, respectively. Only the periplasmic region between TM1 and TM2 (solid black shading) are shown. Red shading denotes α-helix; blue shading denotes β-strand; intense color shading represents high-scoring regions (PROF score, 7 to 9); faint color shading represents low-scoring regions (PROF score, 4 to 6). (B) Amino acid sequences of D39:EHA-Cps2C and site-directed mutants. (i) Amino acid sequence of D39:EHA-Cps2C with predicted secondary structure (http://www.predictprotein.org/) superimposed: gray, TM helix; red, α-helix; blue, β-strand. Amino acid numbering ignores the dual HA tag insert to facilitate comparison to the D39:Cps2C sequence. Asterisks indicate highly conserved proline and glycine residues preceding and within TM2. (ii) Amino acid substitutions are indicated. (iii) Phenotypic change resulting from amino acid sequence changes: M, mucoid phenotype; S, small colony phenotype; W, WT; R, rough phenotype.