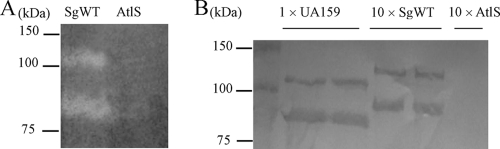
Fig. 2.
(A) Zymographic assay: autolysin profiles of the SgWT and AtlS-deficient strains determined by renaturing SDS-PAGE using a 7.5% polyacrylamide gel containing 1% (wet weight) of cell walls prepared from S. gordonii. (B) Western blot analysis of proteins extracted from SgWT and atlS mutant strains after incubation in 4% SDS extracts. Of note, in order to detect similar signals for the AtlA and AtlS proteins with the anti-AtlA antibody, it was necessary to apply10-fold more surface protein extract from S. gordonii to the gel than is required for S. mutans (Fig. 2B). Thus, duplicate lanes labeled 1 × UA159 contain proteins extracted from S. mutans UA159. Duplicate lanes labeled 10 × SgWT and lanes labeled 10 × AtlS indicate that 10-fold more protein from the wild-type strain or atlS mutant of S. gordonii, respectively, was loaded on the gel than in the S. mutans lanes. Following SDS-PAGE, proteins were transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane and subjected to Western blotting using an affinity-purified anti-AtlA polyclonal antiserum at a dilution of 1:500. See Materials and Methods for more details.