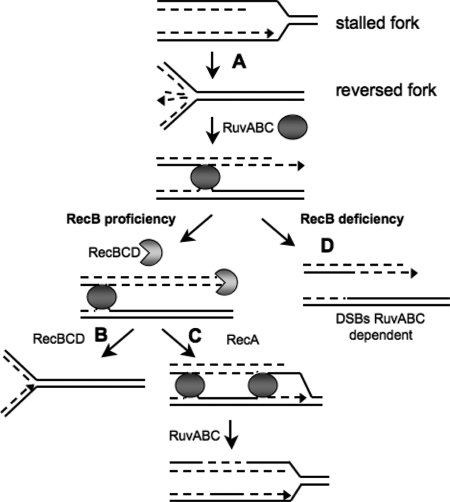
Fig. 1.
Fate of the stalled forks. In the first step (A), the replication fork is arrested, causing fork reversal and forming an HJ. In recombination-proficient cells (B), RecBCD initiates RecA-dependent homologous recombination, and RuvABC resolves the resulting double HJ. In the absence of RecBCD (C), resolution of the HJ by RuvABC leads to DSBs at the stalled replication fork. Solid line, parental chromosome; dashed line, newly synthesized strand; solid disk, RuvAB; incised disk, RecBCD.