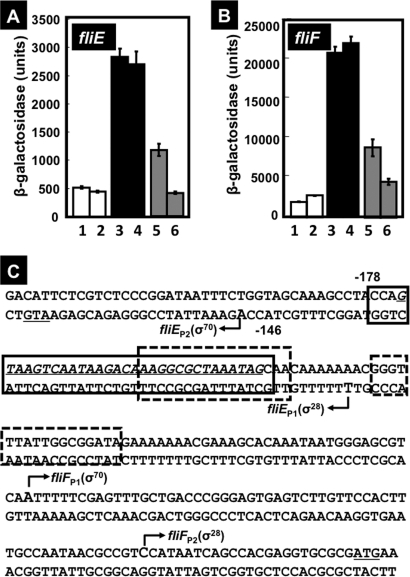
Fig. 9.
Effects of CsgD on the fliE and fliF promoters. (A) E. coli BWWfliE (lanes 1 and 2) and BWcsgDfliE (lanes 3 to 6) strains were transformed with either pBAD18 (lanes 1 to 4) or pBADcsgD (lanes 5 and 6), grown in YESCA medium at 28°C for 8 h (lanes 1, 3, and 5) or 24 h (lanes 2, 4, and 6), and β-galactosidase activities were determined. (B) E. coli BWWfliF (lanes 1 and 2) and BWcsgDfliF (lanes 3 to 6) strains were transformed with either pBAD18 (lanes 1 to 4) or pBADcsgD (lanes 5 and 6), grown in YESCA medium at 28°C for 8 h (lanes 1, 3, and 5) or 24 h (lanes 2, 4, and 6), and β-galactosidase activity was assayed. (C) Locations of CsgD-binding sites within the spacer region between fliE and fliF. The CsgD-binding site of CsgD is indicated by the solid-lined box, while two binding sites of FlhDC, the activator for the fliE and fliF operons, are indicated by the boxes with dotted lines. The fliE and fliF operons are both transcribed by both σ70 and σ28 RNA polymerases.