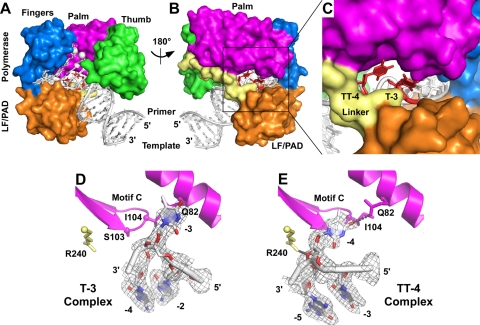
Fig. 3.
Crystal structures of Dpo4 with extrahelical template bases. Superimposed structures of the Dpo4 T-3 and TT-4 ternary complexes are shown as a front overview (A), back overview (B), and view of the gap between the polymerase domain and the LF/PAD (C). The structures of the individual bulged template bases are shown for the T-3 complex (D) and the TT-4 complex (E), together with surrounding protein structures that are mentioned in the text. The gray mesh shows 2Fo-Fc electron density contoured at 1.0 sigma. Dpo4 protein domains are colored as follows: palm (magenta), thumb (green), fingers (blue), LF/PAD (orange), linker (pale yellow). (A to C) The extrahelical nucleotides are colored red, with the remaining DNA shown in white. (A) The white spheres are the two calcium ions bound at the polymerase active site. (D and E) The small spheres mark the positions of the C-alpha atoms of the amino acids shown in stick representation, and the DNA is colored by atom type, as follows: oxygen (red), nitrogen (blue), carbon and phosphate (white). Gray dotted lines indicate hydrogen bonds.