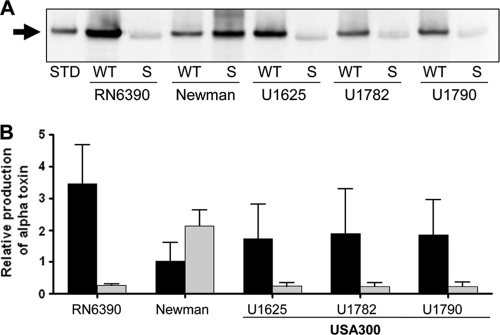
Fig. 1.
Impact of sarA on the alpha-toxin phenotype of stationary-phase cultures. (A) Western blot using alpha-toxin antibody and stationary-phase supernatants from the indicated wild-type (WT) strains and their isogenic sarA (S) mutants. UAMS-1625 (U1625), U1782, and U1790 are isolates of the USA300 clonal lineage (Table 1). STD, alpha-toxin standard. (B) Production of alpha-toxin was assessed by Western blotting of stationary-phase supernatants. Results obtained with each wild-type strain (black) and its isogenic sarA mutant (gray) were quantified with Image J and are shown relative to the signal observed with 50 ng of purified alpha-toxin, the amount of which was set to a value of 1.0. Results are shown as the average ± standard deviation from three independent experiments.