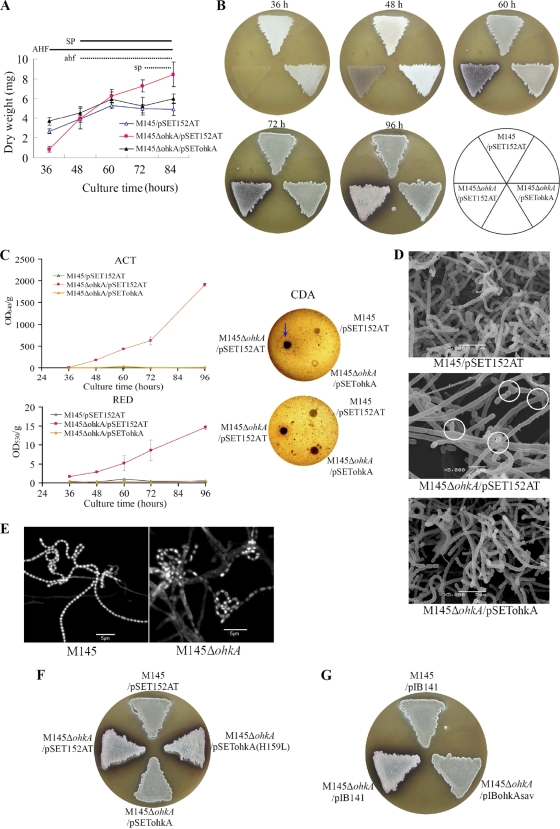
Fig. 1.
Phenotypes of the ohkA deletion mutant compared with the wild-type strain M145. (A) Pregerminated spore suspensions from S. coelicolor M145/pSET152AT (▵), the ohkA mutant (M145ΔohkA/pSET152AT; ▪), and the complemented strain (M145ΔohkA/pSETohkA; ▴) were cultured on MS agar with cellophane discs at 30°C. Cultures were taken and dried at the time points indicated. Experiments were done in triplicate. AHF and SP indicate phases of aerial hypha formation and sporulation, respectively, of M145/pSET152AT and the complemented strain, while ahf and sp indicate the corresponding phases of the ohkA mutant (M145ΔohkA/pSET152AT). Growth was calculated as mg (dry weight). (B) Phenotypes of M145/pSET152AT, M145ΔohkA/pSET152AT, and the complemented strain M145ΔohkA/pSETohkA on MS agar. The plates were incubated at 30°C for the indicated time points. The surface of the mutant strain M145ΔohkA/pSET152AT displayed pink color from 72 h onward. (C) Determination of antibiotic production in M145ΔohkA/pSET152AT, relative to M145/pSET152AT and the complemented strain M145ΔohkA/pSETohkA. For ACT and RED measurement, cultures were grown on MS agar at 30°C and taken at the indicated time course; ACT and RED production was calculated as OD640/g and OD530/g (wet weight), respectively. Experiments were performed in triplicate. For CDA, 1-μl spore suspensions with the same OD450 were grown on MS agar at 30°C for 48 h and then overlaid with Staphylococcus aureus-seeded soft LB agar with (upper panel) or without (lower panel) Ca(NO3)2. A zone of inhibition (indicative of CDA activity) was detected in the presence of Ca(NO3)2, which is indicated by the blue arrow. (D) Scanning electron micrographs (SEM) showing the developmental changes of the S. coelicolor ohkA mutant (with pSET152AT) compared with M145 (with pSET152AT) and the complemented strain M145ΔohkA/pSETohkA. Cultures were grown on MS medium for 4 days at 30°C. Branched aerial hyphae are shown by white circles. Scale bars are shown in the panels. (E) DNA content of S. coelicolor M145 and the ohkA mutant revealed by DAPI staining. The ohkA mutant is disturbed by DNA condensation and segregation. DNA staining was uneven in the ohkA mutant, with only a few spores very strongly stained (indicated by white arrows) and the majority of them weakly stained. Cultures were grown on MS agar for 4 days at 30°C. (F) Spore suspensions of M145/pIB141, M145ΔohkA/pIB141, the complemented strain M145ΔohkA/pSETohkA, and the mutant strain with plasmid-borne mutated ohkA (H159L) (M145ΔohkA/pSETohkAH159L) were plated on MS medium and incubated at 30°C for 4 days. The surface of the mutant strains M145ΔohkA/pSET152AT and M145ΔohkA/pSETohkAH159L showed pink color. (G) Spore suspensions of M145/pIB141, M145ΔohkA/pIB141, and the complemented strain M145ΔohkA/pIBohkAsav were plated on MS medium and incubated at 30°C for 4 days. The impaired morphological differentiation of the ohkA mutant could be complemented by the introduction of the ohkA-homologous gene ohkAsav from S. avermitilis.