Fig. 5.
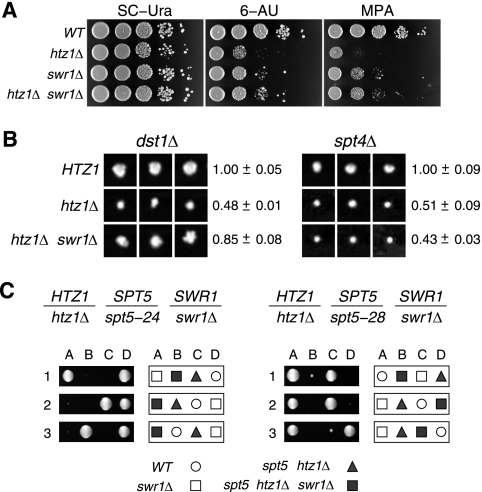
SWR1 partially contributes to elongation phenotypes in the absence of Htz1. (A) swr1Δ is sensitive to the elongation inhibitor drugs 6-azauracil (6-AU) and mycophenolic acid (MPA) and partially suppresses the hypersensitivity of htz1Δ. Tenfold serial dilutions of cultures of each of the indicated strains were spotted on permissive media (SC-Ura), 6-AU media, and MPA media. (B) swr1Δ partially suppresses the synthetic growth defect of htz1Δ dst1Δ double mutants but not htz1Δ spt4Δ double mutants. Synthetic genetic analysis was carried out on a miniarray of deletion strains that are synthetic lethal with htz1Δ (see Materials and Methods). The pinned spots from three independent biological replicates are shown for crosses of dst1Δ and spt4Δ strains against the strains indicated to the left. The averages and standard deviations of the colony growth sizes are shown to the right. (C) swr1Δ fails to suppress the synthetic lethality of htz1Δ spt5-24 and only weakly suppresses htz1Δ spt5-28. Diploid strains with the genotypes shown at the top were sporulated, and the resulting tetrads were dissected. The four spore colonies (A to D) from three representative tetrads (1 to 3) are shown for each cross. Keys to the relevant spore colony genotypes are shown at the bottom.