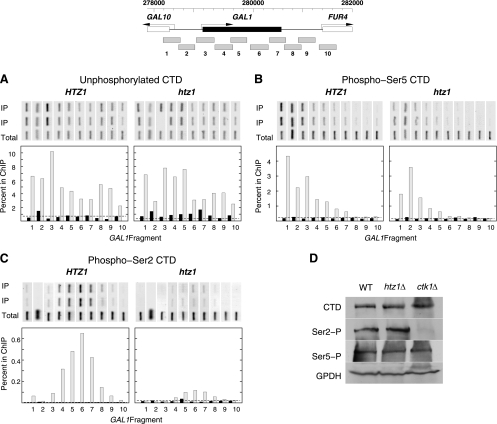
Fig. 6.
Ser2 CTD phosphorylation over the GAL1 ORF is partially dependent on Htz1. (A to C) ChIP analysis of unphosphorylated CTD (antibody 8WG16) (A), phospho-Ser5 (antibody H14) (B), and phospho-Ser2 (antibody H5) (C) at the GAL1 locus in HTZ1 wild-type (MSY2301) and htz1Δ (MSY2302) strains. A diagram of the GAL1 locus, illustrating the locations of the 10 fragments assayed by PCR, is given at the top. For each panel, the PCRs are shown on top. Duplicate reactions were run for each immunoprecipitated sample (IP), and one reaction was performed for the total input chromatin sample (total). Quantification of the ChIP results is shown below as the percentages of input chromatin immunoprecipitated for the 10 fragments across the locus. Black bars, cells before galactose induction; gray bars, cells after 1 h of galactose induction. In each plot, the dashed line shows the ChIP results for a control nontranscribed region of chromosome V. The results shown are representative of three independent experiments for the unphosphorylated CTD, three for the Ser5-P CTD, and four for the Ser2-P CTD. (D) Global levels of Ser2, Ser5, and the unphosphorylated CTD are not affected by htz1Δ. A Western blot of whole-cell extracts of the indicated strains was probed with H5 (anti-Ser2), H14 (anti-Ser5), and 8WG16 (unphosphorylated CTD). Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase was used as the loading control. The ctk1Δ strain is from the systematic deletion collection strain (EUROSCARF).