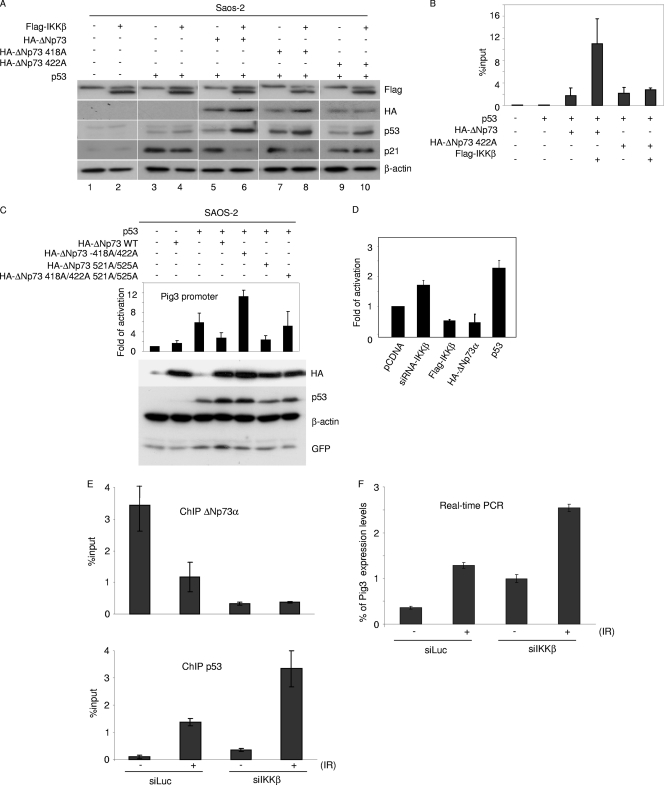
Fig. 6.
IKK-mediated phosphorylation of ΔNp73α increases its p53 inhibitory activity. (A) Saos-2 cells were transfected with different pcDNA3 constructs in the indicated combinations. After 24 h, protein extracts were analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (B) Saos-2 cells were transfected with different pcDNA3 constructs in the indicated combinations. After 36 h, ChIP was performed using an anti-HA-tag antibody and followed by real-time PCR, using primers flanking the p53 RE within the p21 promoter. Simultaneously, 1/10 of the total chromatin was processed. The values in the histogram were obtained by dividing for each sample the amount of p21 promoter which is bound by ΔNp73-HA by the total amount of p21 promoter present in the input. (C) Saos-2 cells were transfected with the following constructs: Pig3prom-firefly luciferase reporter construct, a constitutively expressing Renilla construct, pcDNA3-HA-ΔNp73α (wild type or 418A/422A, 521A/525A, or 418A/422A/521A/525A mutant), pcDNA-p53, and pE-GFPCI. After 24 h, cells were collected and processed for the luciferase assay as described in Materials and Methods (upper panel). In parallel, protein extracts were prepared and analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies (lower panel). (D) 38E6E7HFK cells were transfected with the following constructs: Pig3prom-firefly luciferase reporter construct and a constitutively expressing Renilla construct, in combination with siRNA-IKKβ, Flag-IKKβ, pCDNA HA-ΔNp73α, or pcDNA-p53. Thirty-six hours posttransfection, cells were collected and lysed. Luciferase activity was measured and expressed as fold activation in comparison to that of the control (pCDNA). The variation in fold activities between the different conditions was significant (P < 0.05). (E and F) 38E6E7HFK cells were transfected with siIKKβ or siLuc as a negative control; 24 h posttransfection, cells were treated with ionizing radiations (IR) (30 Gy). After irradiation, cells were allowed to grow for 8 h and processed for ChIP (E) or gene expression analysis (F). ChIP followed by real-time PCR was performed using an anti-ΔNp73 antibody (upper panel) or anti-p53 antibody (lower panel) and with primers flanking the p53-RE within the pig3 promoter. Simultaneously, 1/10 of the total chromatin was processed. The values reported in the histogram were obtained as for panel B (E). Pig3 mRNA levels in cells subjected to the indicated treatments were determined by real-time RT-PCR (F).