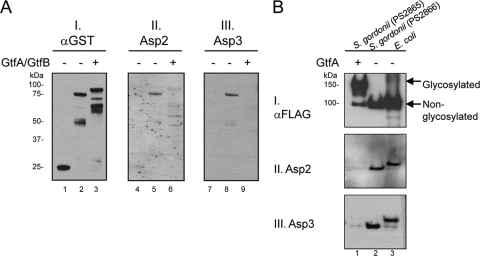
Fig. 6.
Glycosylation of GspB prevents Asp binding. (A) A GST-SRR1-BR fusion protein was expressed in E. coli, either with or without the coexpression of the streptococcal glycosyltransferases GtfA and GtfB (35). After purification, the constructs were probed by far-Western blotting with purified H6Asp2 or H6Asp3. Lanes 1, 4, and 7, GST; lanes 2, 5, and 8, nonglycosylated GST-SRR1-BR; lanes 3, 6, and 9, glycosylated GST-SRR1-BR. The amount of fusion protein present on the blots was assessed with anti-GST antibody (blot I). GspB binding by Asp2 or Asp3 was detected with anti-H6 antibody (blots II and III). (B) GspB736FLAG was expressed from S. gordonii in the presence or absence of GtfA (lanes 1 and 2, respectively) and purified from the culture medium. The proteins were probed by far-Western blotting with purified H6Asp2 or H6Asp3, as indicated. Nonglycosylated GspB736FLAG purified from the WCL of E. coli served as a positive control (lane 3). The amount of protein present on the blot was assessed with anti-FLAG antibody (blot I). Note that nonglycosylated GspB736FLAG secreted into the culture medium of M99 lacks the signal peptide and thus has a lower molecular mass than the recombinant form obtained from E. coli.