Fig. 2.
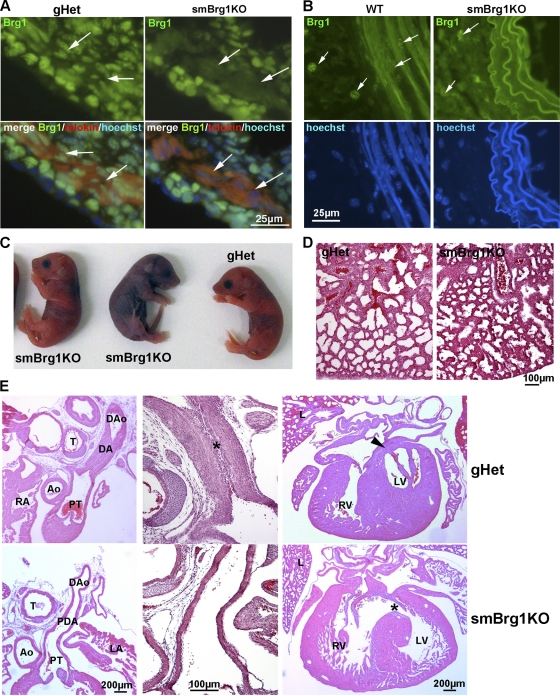
Smooth muscle-specific knockout of Brg1 causes cardiovascular and pulmonary defects. (A) Immunofluorescent analysis of protein expression. Anti-Brg1–fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) (green), MLCK/telokin-rhodamine (red), and nuclear Hoechst (blue) immunofluorescence staining of colon cryosections from 2-day-old smBrg1 knockout (Brg1f/− smMHC-Cre−/+) and littermate control (Brg1f/− smMHC-Cre−/−) mice is shown. The smooth muscle layer is identified by the strong staining for MLCK/telokin. Arrows point to examples of cells within this smooth muscle layer. (B) Immunofluorescence staining of Brg1 (green) and nuclei (Hoechst) in aorta cryosections from 4- to 5-week-old smBrg1 knockout (Brg1f/− smMHC-Cre−/+) and littermate wild-type (Brg1f/+ smMHC-Cre−/−) mice. (C) Images of newborn smBrg1 knockout and global heterozygous mice as indicated. The blue coloration in the middle mouse is indicative of poorly oxygenated blood. (D) H&E staining of the lung from a noncyanotic global Brg1 heterozygous mouse (gHet) and a cyanotic smBrg1 knockout mouse. (E) Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) and interventricular septal defects (VSDs) in cyanotic smBrg1 knockout mice. Upper panels, transverse H&E-stained sections of torsos of global Brg1 heterozygous mice (n = 3) at postnatal day 1 showed expected normal closure of the ductus arteriosus (DA) in continuity within the descending aorta (DAo). At high power, intimal thickening in the form of proliferation of luminal endothelium and migration of medial smooth muscle cells was apparent in the DA (*). There is also the expected fused septum separating the left and right ventricles (arrowhead). Lower panels, transverse H&E-stained sections of torsos of smBrg1KO mice (n = 4) at postnatal day 1 showed patent ductus arteriosus (the PDA connects the main pulmonary artery to the descending aorta). At high power, DAs from smBrg1KO mice showed a single endothelial layer with an open lumen that was covered by a layer of normal intimal thickening. Additionally, there is also abnormal communication between left and right ventricles (*). Ao, aorta; PT, pulmonary trunk; RA, right atria; LA, left atria; T, trachea; RV, right ventricle; LV, left ventricle; L, lung.