Fig. 1.
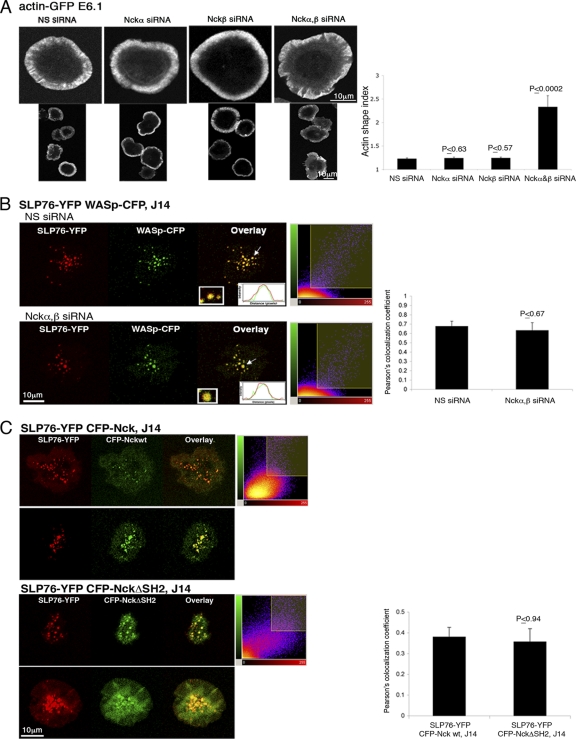
Actin polymerization and the recruitment of WASp to SLP76 signaling clusters are not solely dependent on Nck. (A) Cells were plated, fixed, and stained with phalloidin. Confocal images were collected after 5 min of activation. In the right panel, the results of >4 independent experiments are presented The actin shape index was determined as described in Materials and Methods. t tests were performed to compare the results of nonspecific (NS) siRNA treatment with the results for other experimental groups; error bars show standard errors. (B) SLP76-deficient J14 cells expressing SLP76-YFP and WASp-CFP were treated with siRNA specific to Nckα,β. Cells treated with NS siRNA served as a negative control. After 48 h, cells were plated and activated for 3 min as described for panel A. Overlays (insets) of the fluorescence peaks of the punctae are shown. Colocalization analysis is based on these fluorescence intensity peaks and was further analyzed by obtaining Pearson's colocalization coefficients (scatter diagrams). Imaging analysis was performed on more than 50 cells for each experimental group. (C) The association of Nck with SLP76 is not exclusively dependent on the Nck SH2 domain. J14 T cells expressing SLP76-YFP and the indicated CFP-Nck forms (wt or SH2 domain deletion [NckΔSH2]) were seeded on stimulatory coverslips. Live-cell images were collected 3 min after activation. Two out of 30 cells are presented for each experimental group. The combined images (overlays) are presented. A t test was performed, comparing the colocalization of CFP-Nck wt clusters with SLP76-YFP to the colocalization of the CFP-NckΔSH2 mutant with SLP76-YFP.