Fig. 1.
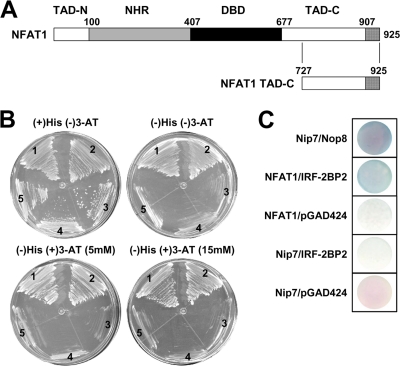
IRF-2BP2 interacts with NFAT1 TAD-C in a yeast two-hybrid assay. (A) Schematic representation of the NFAT1 transcriptional factor with its conserved domains: the NFAT homology region (NHR), the DNA binding domain (DBD), and the transactivation domains (TAD-N and TAD-C). The boundary of each region is labeled above the sequence; numbering refers to the amino acid position of the protein. The NFAT1 C-terminal end (amino acids 727 to 925) used in the yeast two-hybrid system also is represented. (B) Yeast two-hybrid system interaction assays on plates containing synthetic minimal medium and 0, 5, or 15 mM 3-AT. Region 1, positive control (pTL-Nip7p + pACT-Nop8p); region 2, test (pTL-CT-NFAT1 + pACT-IRF-2BP2); regions 3, 4, and 5, negative controls (pTL-CT-NFAT + pGAD424, pBTM-Nip7 + pGAD-IRF-2BP2, pBTM-Nip7 + pGAD-424, respectively). (C) β-Galactosidase filter assay. The L40 strain, which contains the HIS3 and lacZ reporter genes, was cotransformed with vectors containing the LexA DBD fusion proteins and Gal4p activation domain fusion proteins. All results are representative of at least three independent experiments.