Fig. 1.
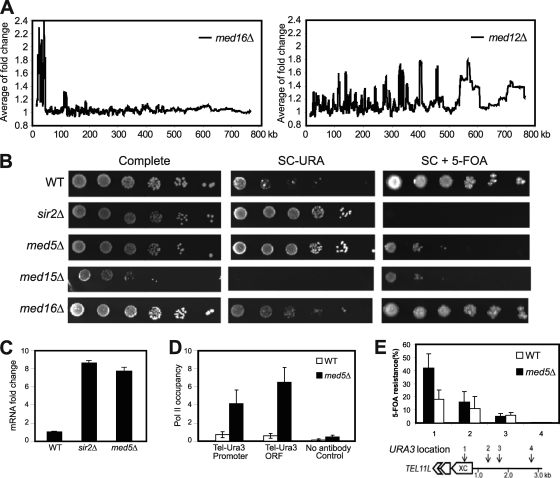
Deletion of Mediator components disrupts transcription silencing at telomeres. (A) Moving average analysis of gene expression changes in med16Δ and med12Δ mutant strains. The distance from a gene to the telomere was calculated based on the position of the translation start site. The window size is 150. (B) Fivefold dilutions of the indicated deletion strains were spotted on complete medium, on synthetic complete medium lacking uracil (SC−URA), and on synthetic complete medium containing 5-FOA (SC + 5-FOA). All strains (UCC3505, CGC209, CGC210, CGC211, and CGC212) contained the URA3 reporter gene inserted at tel7L. (C) Real-time PCR analysis shows fold changes of tel7L URA3 gene transcription in strains UCC3505, CGC210, and CGC209. (D) A ChIP assay using the 4H8 antibody followed by real-time PCR analysis shows Pol II occupancy at URA3 promoter and coding regions of the indicated strains. Background values were calculated using a no-antibody control. Error bars indicate standard deviations based on experiments from at least three independent cultures. (E) The X core elements of telomeres show silencing defects in med5Δ cells. The positions (1 to 4) of URA3 gene insertions near tel11L are indicated. Silencing assays were performed with wild-type and med5Δ cells bearing the URA3 gene inserted at positions 1 to 4. The extent of silencing is expressed as the fraction of cells resistant to 5-FOA (n = 4). Error bars shows standard deviations. (Schematic diagram adapted from reference 7 with permission of the publisher.)